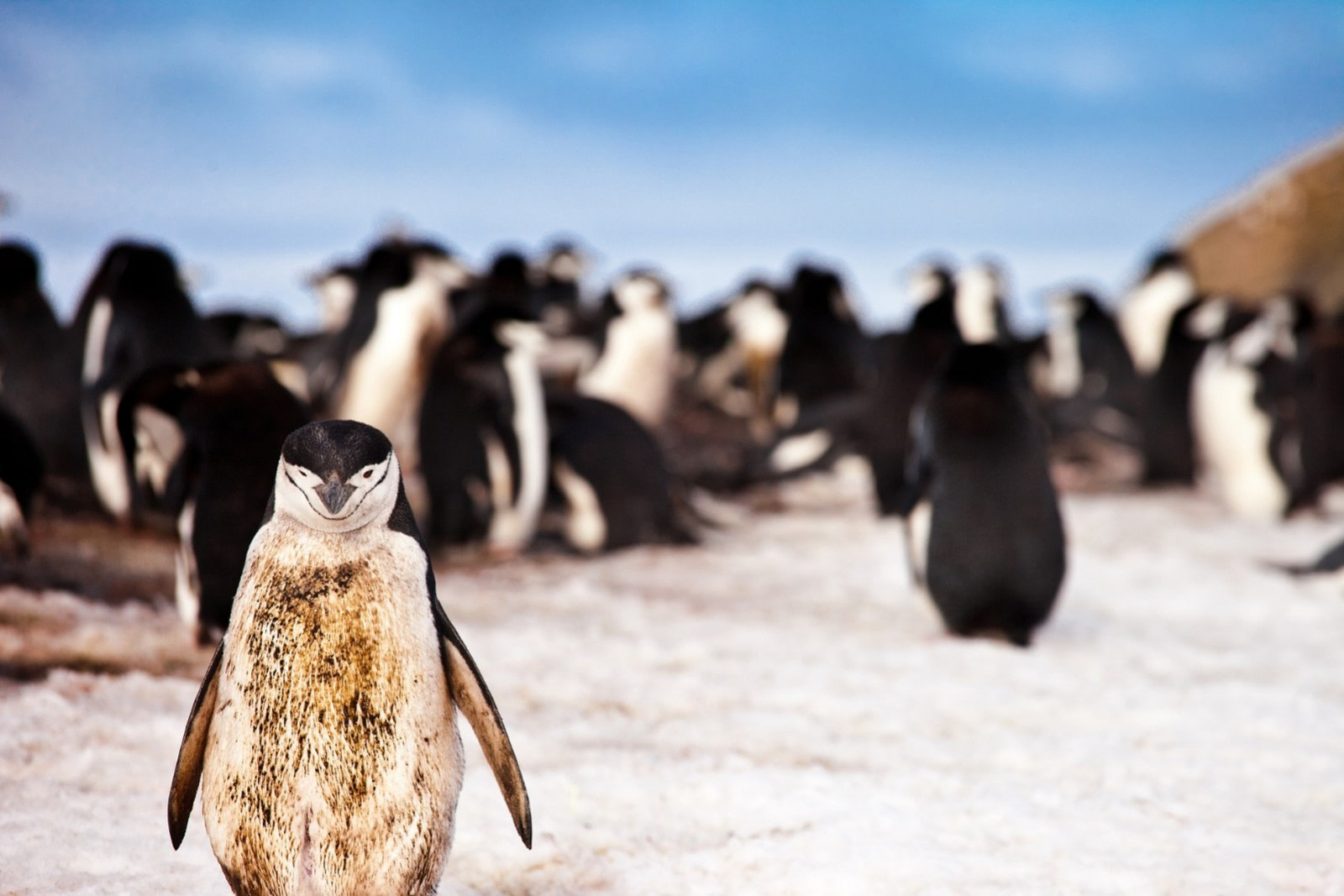
Approximately 50 million years ago, Antarctica was detaching from the vast supercontinent of Gondwana, and penguins were emerging as a distinct species. Initially native to warmer regions, they gradually adapted to the cooling climate of Antarctica as they ventured further south.
Today, there are 17 penguin species globally, but only eight species inhabit Antarctica and the sub-Antarctic islands: chinstraps, emperors, Adélies, gentoos, kings, Magellanics, rockhoppers, and macaronis. Here, we explore some common penguin facts that apply to all species of these beloved flightless seabirds.

1. Penguins are flightless seabirds
Penguins are flightless birds that thrive both on land and in the sea. Unlike flying birds, which molt and replace feathers gradually to stay airborne, penguins molt all at once over two to five weeks during the austral summer.
This rapid molting allows penguins to return to the sea without losing insulation. Molting is crucial for penguins as they lose many feathers through preening, contact with other penguins, and interaction with water and terrain. Once new feathers grow, penguins are ready to head back to sea.

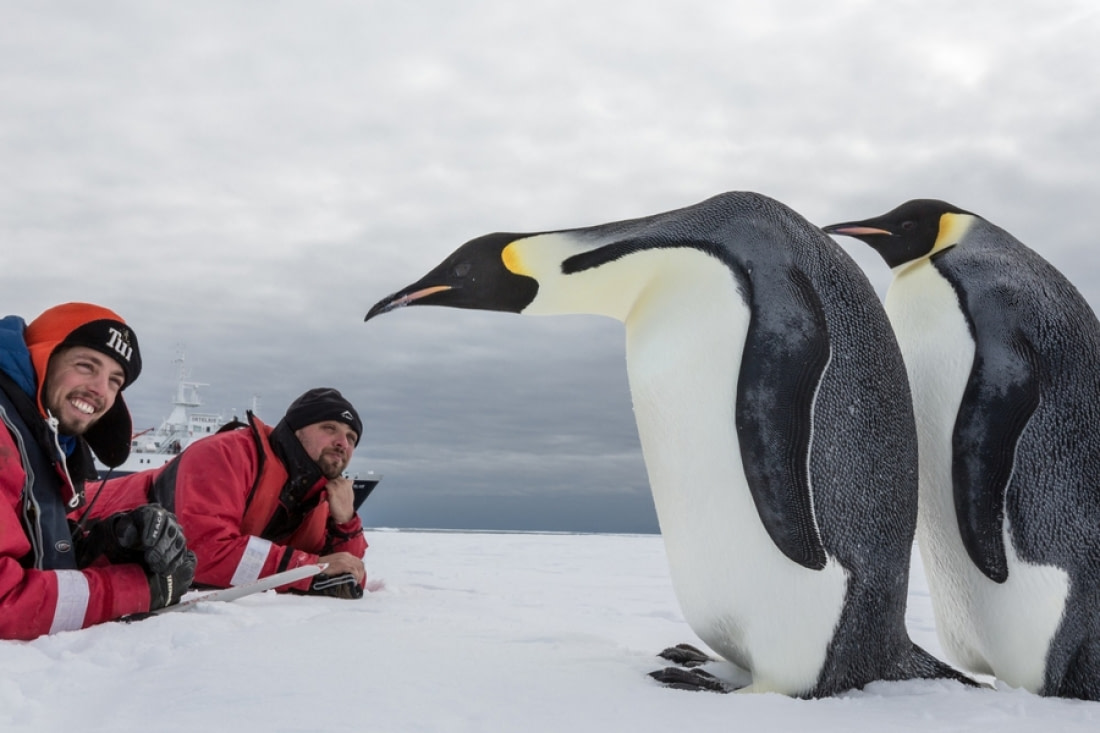
2. Swimming is a particular penguin talent
Penguins have evolved their wings into flippers, making them excellent swimmers. They possess well-developed breast and wing muscles to navigate through dense water. To aid in swimming, penguin blood contains hemoglobin adapted to transport large volumes of oxygen.
Additionally, their muscle tissues contain a high volume of myoglobin, allowing efficient oxygen storage underwater. Penguins swim with their heads close to their shoulders and feet near their tails, maintaining a compact body for minimal water resistance. They have better underwater vision than on land.
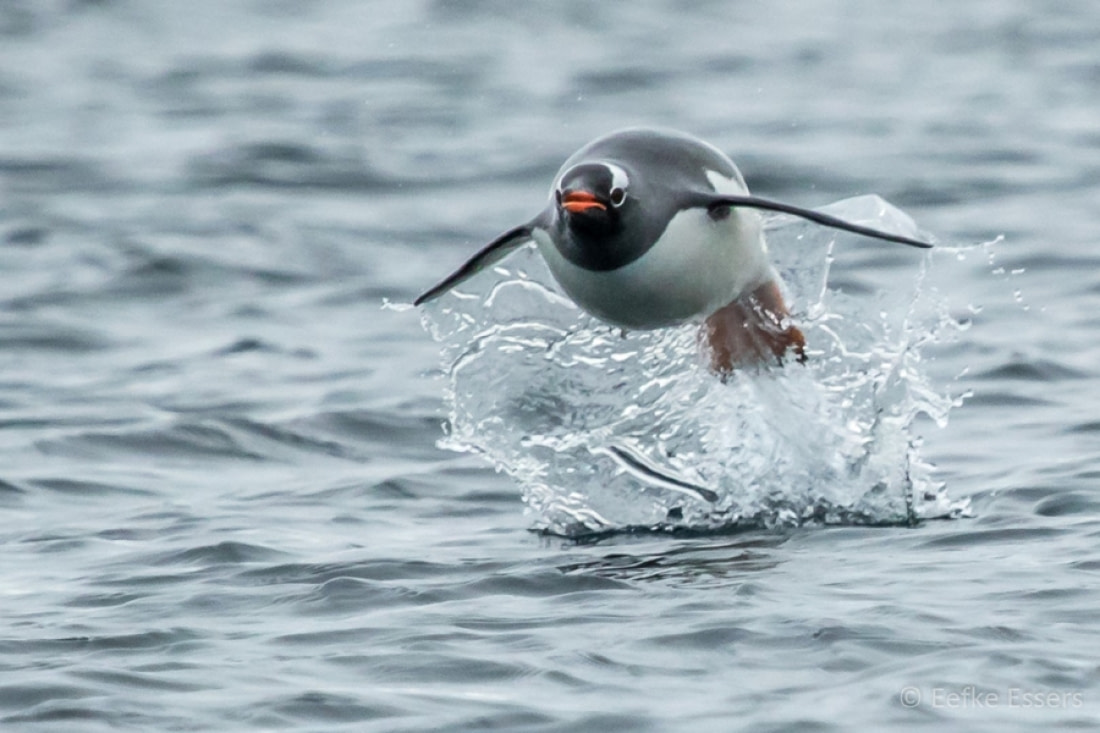

3. Penguins have an open diet
Penguins primarily consume krill, a shrimp-like creature also favored by whales. However, they also eat squid and fish. During the summer, southern penguin species often feed on Antarctic silverfish, the most abundant small fish in the shallow coastal waters off Antarctica.
King and emperor penguins, two of the most cherished species, also feed on lantern fish in addition to krill. Emperor penguins are particularly determined hunters, known to forage several hundred kilometers from their colonies.
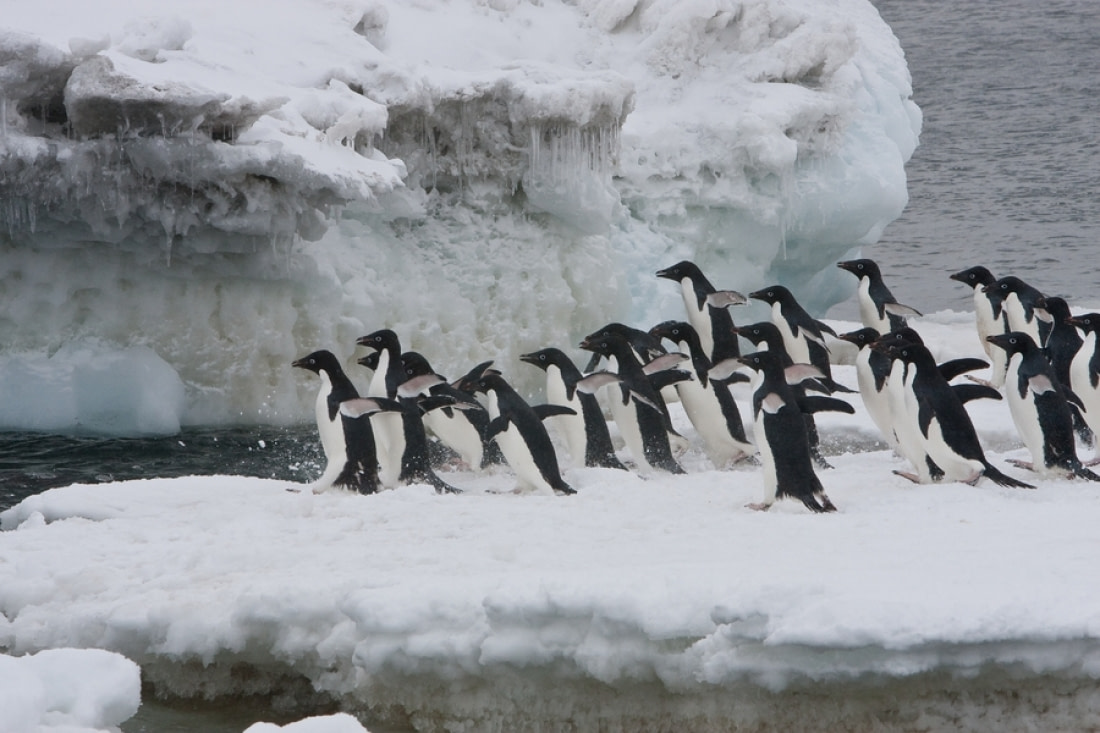

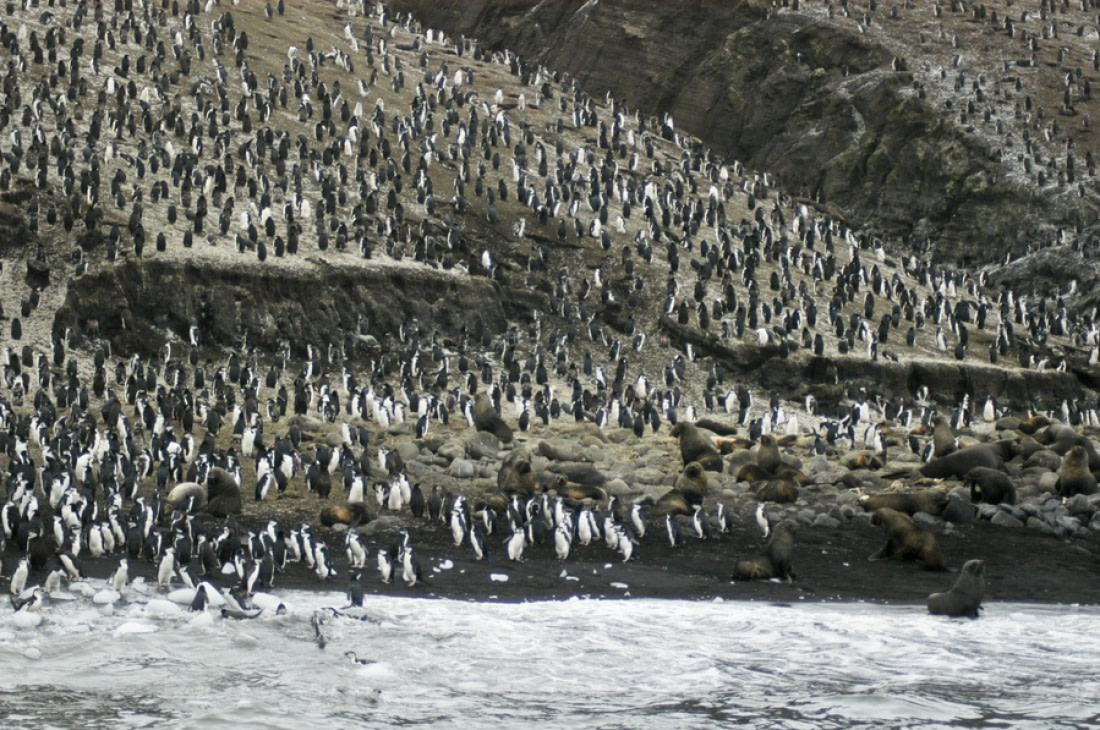
4. Breeding takes place in large penguin colonies
On land, penguins form large colonies that can sometimes contain up to a million nesting pairs. They travel to and from these colonies by walking, swimming, or sliding on their bellies. A lesser-known fact is that Antarctic penguins migrate to their colonies only after storing enough body fat to survive when the pack ice becomes too thick for regular feeding.
Penguins arrive at their breeding colonies in early October, with males arriving first. Colonies reach peak population around early November. It takes between one and 12 days for mates to pair up, and each breeding pair lays between one and three eggs.
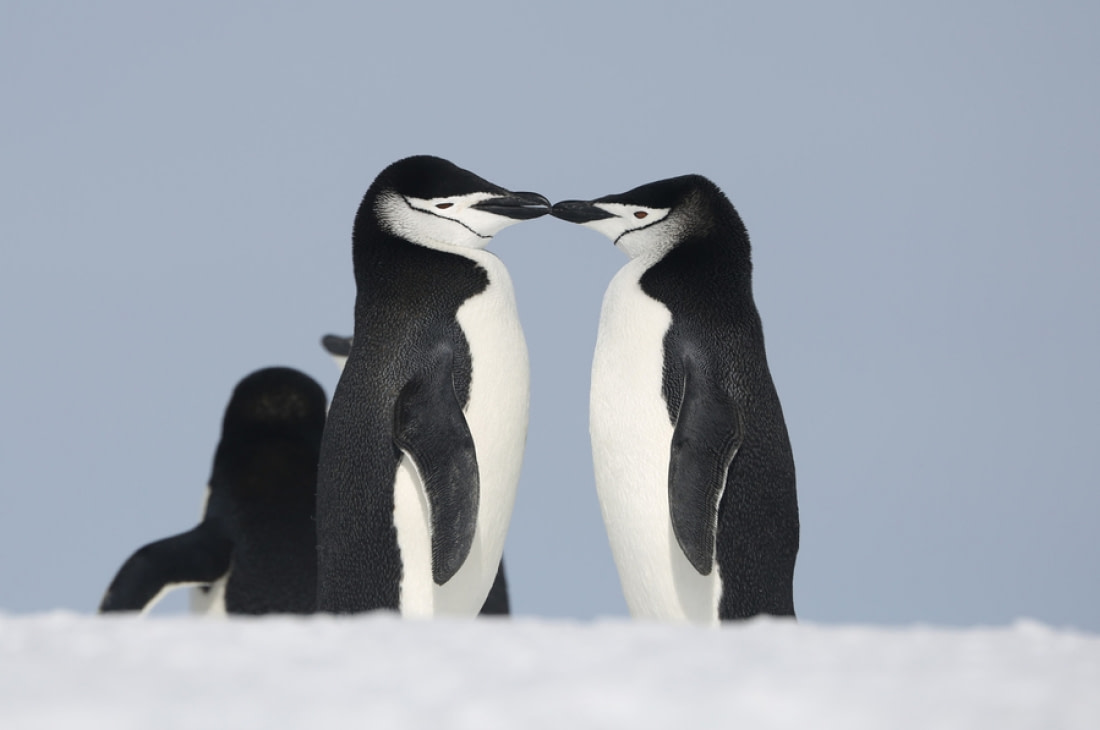

5. Penguins drink salty water
Most penguins live in environments with little or no fresh water, so they have adapted to balance their salt levels. Penguins have a supraorbital gland near their eyes that filters salt out of their systems. As blood passes through the gland, it traps salt before it can travel through the rest of their body. This excess salt mixes with moisture inside the gland, travels down their nasal passage, and drips out of their nose.
Even so, penguins usually prefer fresh water when available. Rockhopper penguins, for instance, tend to live around freshwater sources rather than drink from the sea.
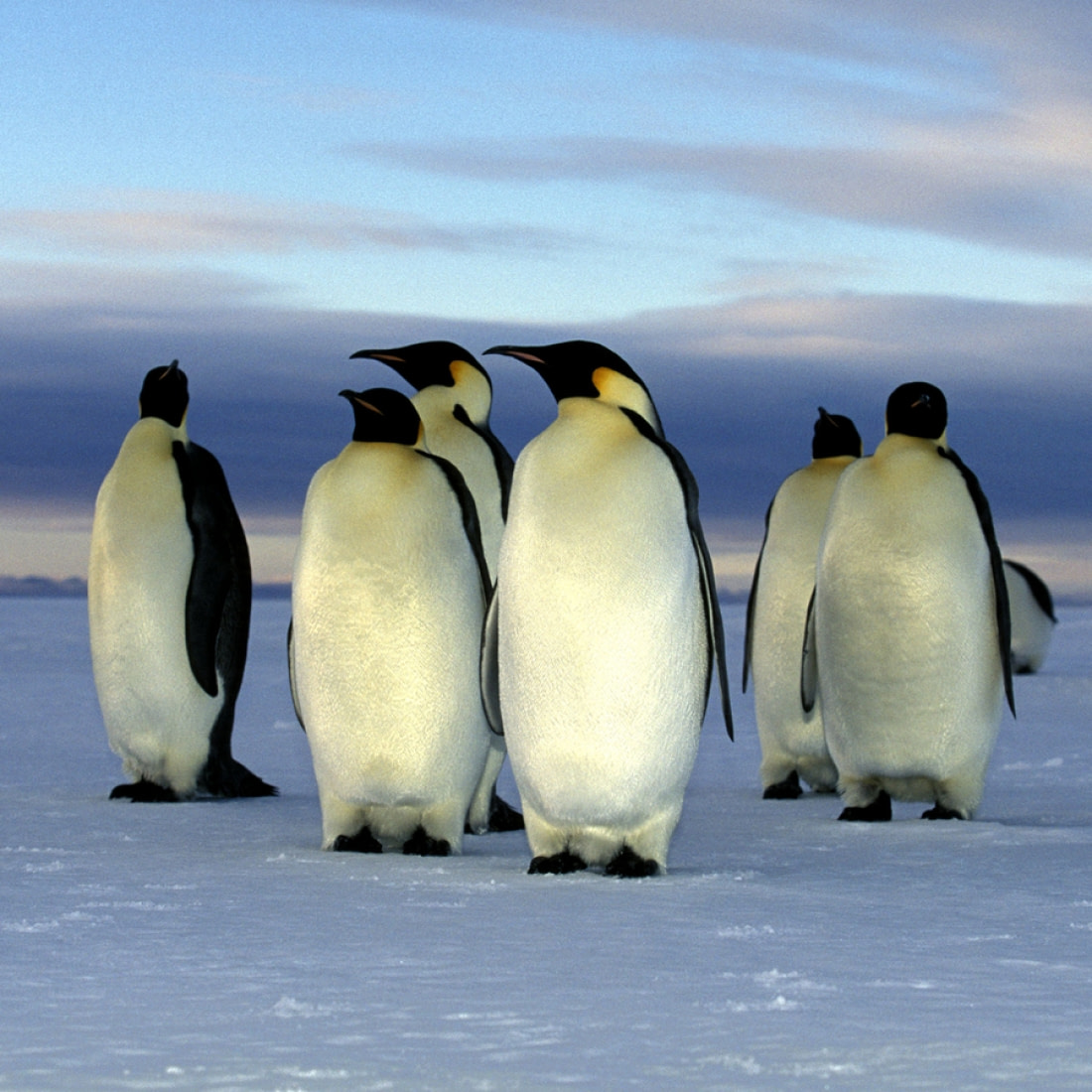

6. Deep dives are a distinct penguin adaptation
Penguins are generally excellent divers, but emperor penguins make the deepest and longest dives of all species. They can dive for 20-30 minutes at a time and reach depths of around 500 meters (over 1,600 feet). To stay underwater that long, penguins have developed the ability to control how and when their muscles use oxygen. They can either starve their muscles for oxygen or give them a boost to keep working during long dives.
To understand how emperor penguins can dive for such long periods, scientists in McMurdo Sound designed special probes to monitor several penguins’ muscles during dives. In 50 recorded dives ranging between 7-64 meters (23-210 feet) deep, the penguins stayed underwater anywhere from 2.3-11.4 minutes.
During deeper dives, researchers found that emperors selectively sent extra oxygen from their blood into their muscles. They can only do this for short periods until blood oxygen levels become too low for the rest of their body, forcing them to surface for air.
The downside of this adaptation is lactic acid build-up, so penguins will only do it if the reward (a good meal) is worth it.

7. Penguin feet don’t freeze on the ice
It may seem obvious that Antarctic penguins are adapted to stay warm in extremely cold environments, but fewer people know how well-adapted their feet are to such temperatures. Penguins have special arteries in their legs that can adjust blood flow in response to foot temperature, sending just enough blood to their feet to prevent freezing.
To maximize their use of body heat, the warm blood on the way to their feet passes the blood returning to their bodies, warming the colder blood before it continues down to their feet. However, because most of a penguin’s body is warm and waterproof due to their fat and feathers, they can easily overheat on sunny days. To stay cool, penguins let heat escape from their beaks and their feet.
For more species-specific Antarctic penguin facts, check out our fascinating Eight Great Penguin Species of Antarctica article.

Blog



Antarctica’s first Marine Protected Area

The Arctic Borderland of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard

Deception Island deceptively active

Svalbard’s 12 Most Iconic Animals

Polar Cuisine in Pictures

The Secret Life of Glaciers: How They Form, Move, and Melt

The secrets of Antarctic seals revealed

Harp seals harping on in Greenland

Life in the Polar Regions

Diving in Antarctica: The Ultimate Underwater Experience

Seven Sublime Antarctic Bays

Arctic vs. Antarctica: A Traveler’s Guide

The Wildlife of Antarctica’s Seas and Skies

The First Buildings in Antarctica: Borchgrevink’s Historic Huts

True South: A New Flag for a Global Antarctica

How Arctic Wildlife Differs from Antarctic

The Small but Social Commerson’s Dolphin

A Day on m/v Plancius

The Ice-Jewelled Geology of Spitsbergen