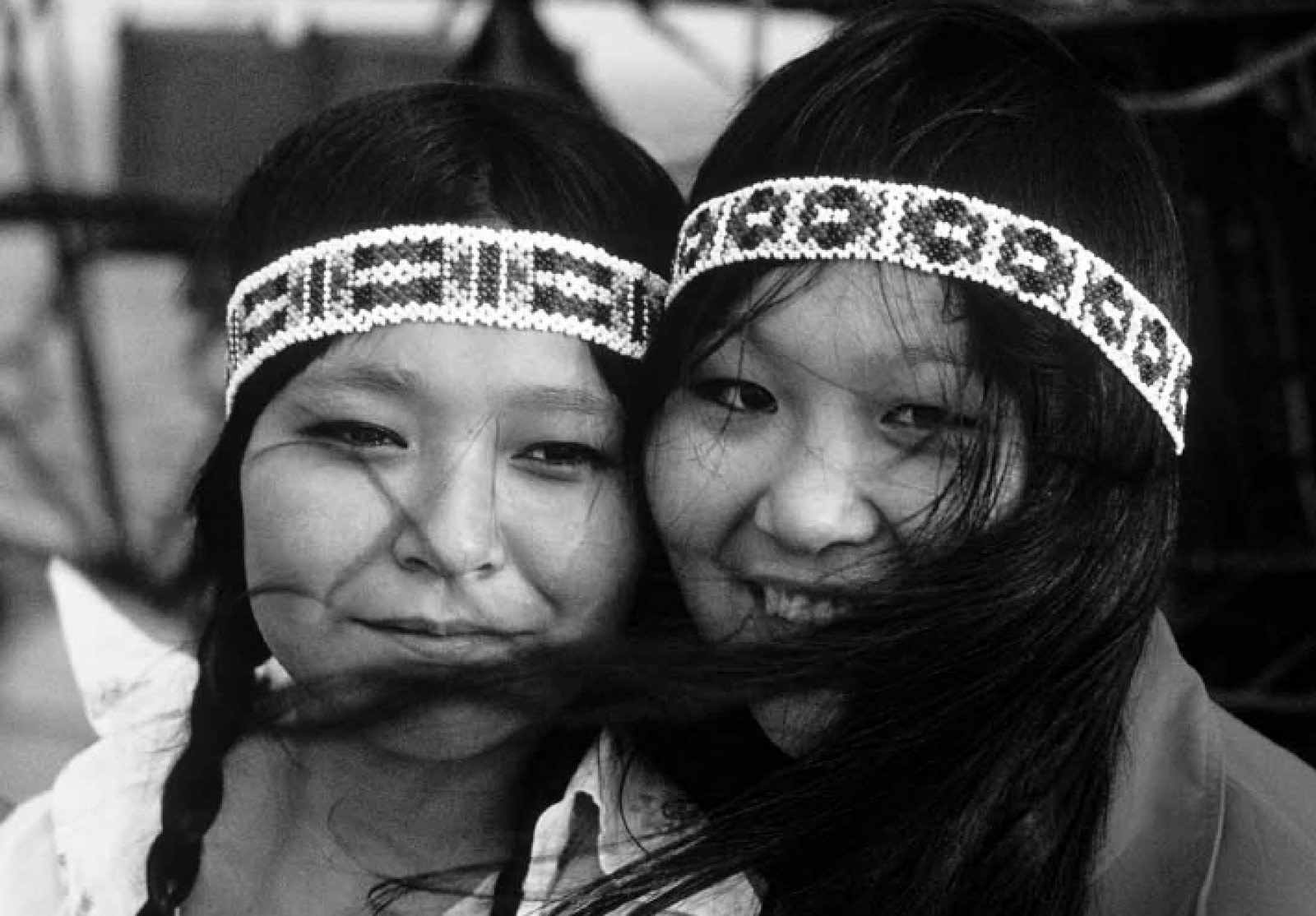
The Inuit are an indigenous Arctic people who speak the languages of the Eskaleutian family and reside in four countries surrounding the North Pole: Greenland, Canada, the United States, and Russia.
Though most Inuit have fully modernized, their ancestors are responsible for many innovations we take for granted today.

Traditional cold-weather Inuit clothing
One of the most longstanding pieces of Inuit clothing is the parka, which enabled past Inuit populations to survive in some of the coldest environments on Earth. In addition to keeping the wearer warm, the Inuit parka also has thread patterns that communicate information about who the Inuit are.
Inuit pants, mittens, and footwear were made from caribou or sealskin that had numerous layers depending on the season.
The Inuit origins of the paleo diet
Some Inuit still have a diet consisting of fish and some land animals, with very little fruit or vegetables. In particular, reindeer, musk ox, Arctic hare, walrus, polar bear, seal, whale, ptarmigan, geese, ducks, and other birds are the typical diet of Inuit.

Inuit igloos and related matters
Igloos were used as a temporary shelter on extended winter hunting trips, not as a permanent Inuit home.
Where the blocks don’t meet, snow was packed in to provide insulation, and a hole was cut at the top for ventilation. For studier construction, Inuit took the snow blocks from snowbanks that had formed in a snowstorm rather than from snowbanks that had accumulated over many snows, as those blocks were more fragile.
Inuit turf huts and summer tents
Turf huts, or Earth huts, were a common form of Inuit dwelling. They were robust and insulated enough to live in permanently.
A typical Inuit hut was low, with walls made of large stones and a roof supported by beams of driftwood. The dwellings were always located near the sea so that the Inuit could easily get to their kayaks when hunting for seals.
During the summer months, Inuit families left the turf huts and gathered berries, hunted reindeer, and caught fish, enabling them to stockpile enough provisions to carry them through the cold and dark winter months.
To avoid sleeping in the open, Inuit traveled with tents made of sealskin that were easy to carry and could be set up anywhere food was found. The tents were supported by a wooden frame made out of driftwood, with an outer sealskin cover.

The Inuit hunter’s kayak
Another key part of Inuit life was the kayak, which means "hunters boat."
In addition to its use for hunting, the Inuit kayak also served as a means of transportation. It was propelled by a double-bladed paddle and was usually made of driftwood or whalebone to ensure a light frame.
Inuit kayaks were typically covered with stretched skins made watertight with whale fat and camouflaged with a white cloth draped over the front.
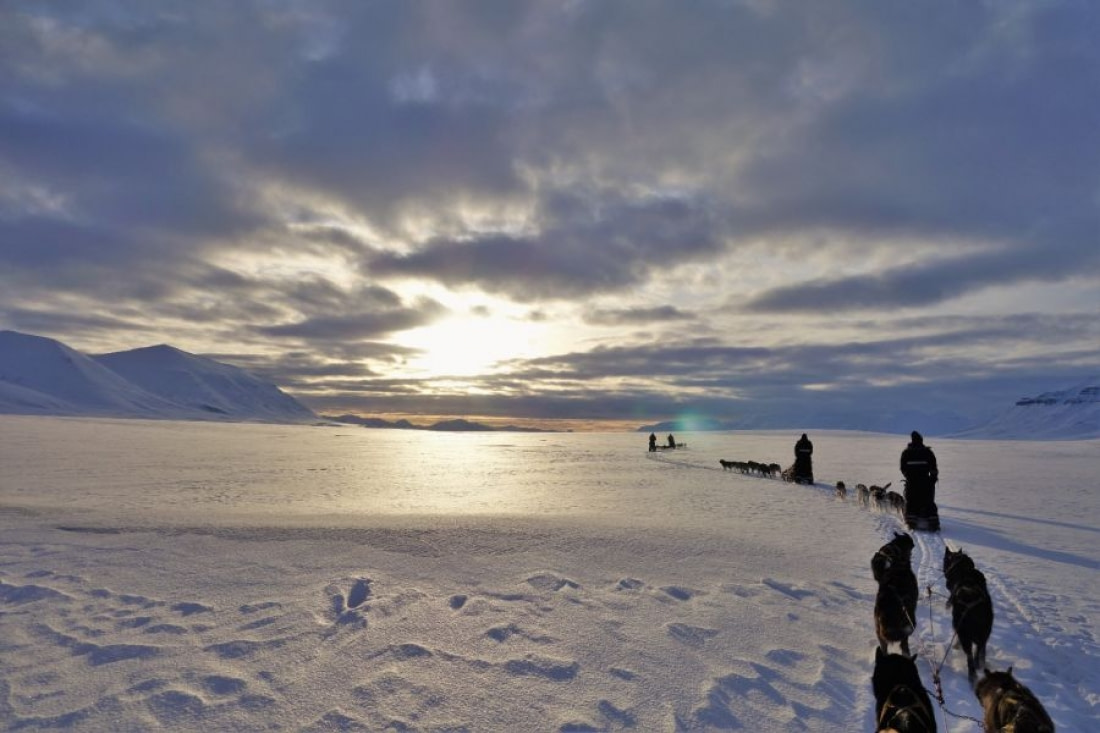
Sledging across the ice Inuit style
One of the most traditional ways for the Inuit to travel across the frozen ice of the Arctic is via the sledge, or qamutik, pulled by Qimmig – the Inuit name for dog.
The traditional Inuit sledge is composed of two wooden runners on which a platform is built. The bottom of the sledge is as smooth as possible to enable it to glide across the ice.
The sledges have cargo beds that are generally constructed in a basket-like style and are elevated above the runners by around 5-6 inches. At the front of the sledge is the brushbow, a piece of wood shaped as a crescent, to clear the way.
The sledge is made of wood as well as reindeer hide and even frozen salmon skin in areas where wood was not available. To steer the sledge the driver simply has handlebars that the sledder can hold on and learn into when turning the sledge.
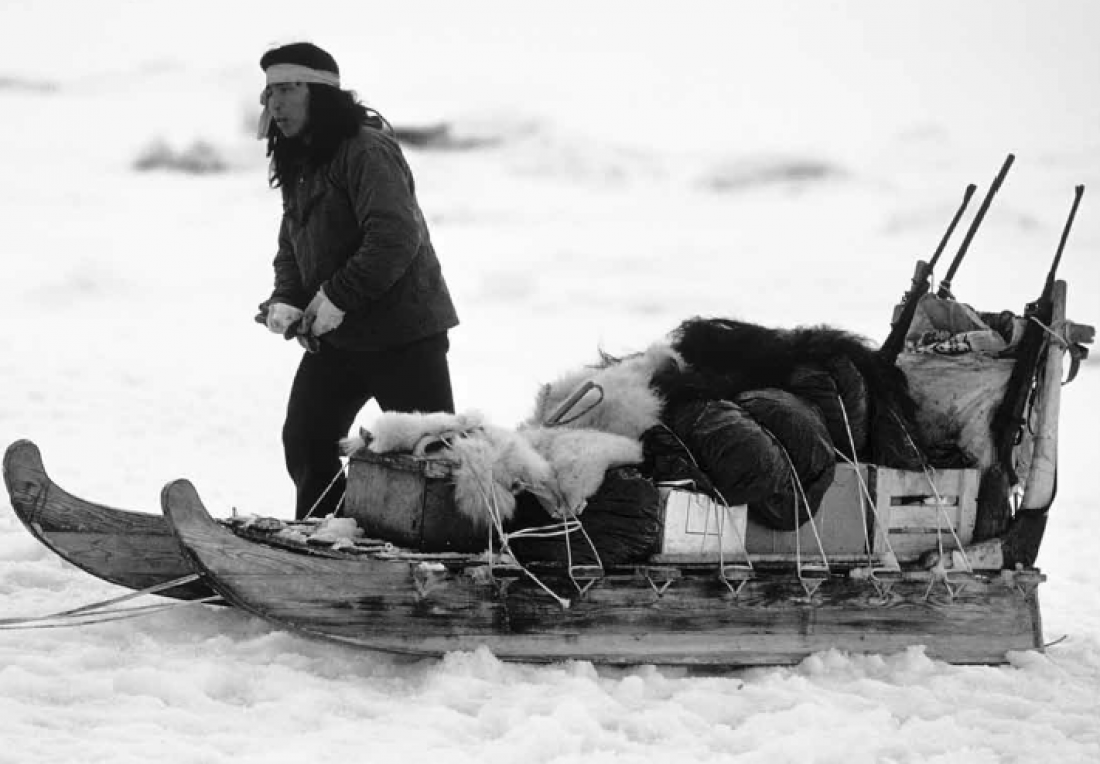

Pack dogs and Inuit sledges
Huskies have been used to pull Inuit sledges since around 800 A.D. Prior to that, the Inuit used these dogs as hunting partners. They also acted as guard dogs, alerting the Inuit to approaching polar bears.
Huskies weren't bred to be racing dogs, but are powerful creatures able to pull up to twice their body weight.
To ensure the dogs are obedient, Inuit utilize a male "boss dog" to lead each pack. There may be two boss dogs that can work cooperatively. The boss dog is the owner’s most valuable asset, as he can rule the pack for many years with minimal bloodshed.
The boss dog prevents or stops fights among lower-ranking dogs and is usually the one that breeds with the females.






Related Trips
Blog



10 Traits of Post-Ice-Age Greenland

Ice streams and lakes under the Greenland Ice Sheet

Tracking Greenland’s Wildlife from Space

Greenland: East vs. West

10 Books and Films To Prepare for your Antarctica cruise

Antarctic Icon: 44 Facts About the Emperor Penguin

Inside the Svalbard Global Seed Vault

Arctic Mythology: Inuit, Saami, and the Ancient Greeks

Five Reasons You Should Cruise the Ross Sea Immediately

Why You Should Visit Greenland: 11 Things to See, Do, and Explore

Living the Antarctic Dream

Large and in Charge: Antarctica’s Southern Elephant Seals

Svalbard vs. the Canadian Arctic

South Georgia in Spring

Antarctic krill: Antarctica's Superfood

The First Overwintering Hut in Antarctica

Antarctica’s first Marine Protected Area

Navigating by touch through the sea ice

An igneous paradise: Franklin Island





 20 Days / 19 Nights
20 Days / 19 Nights

