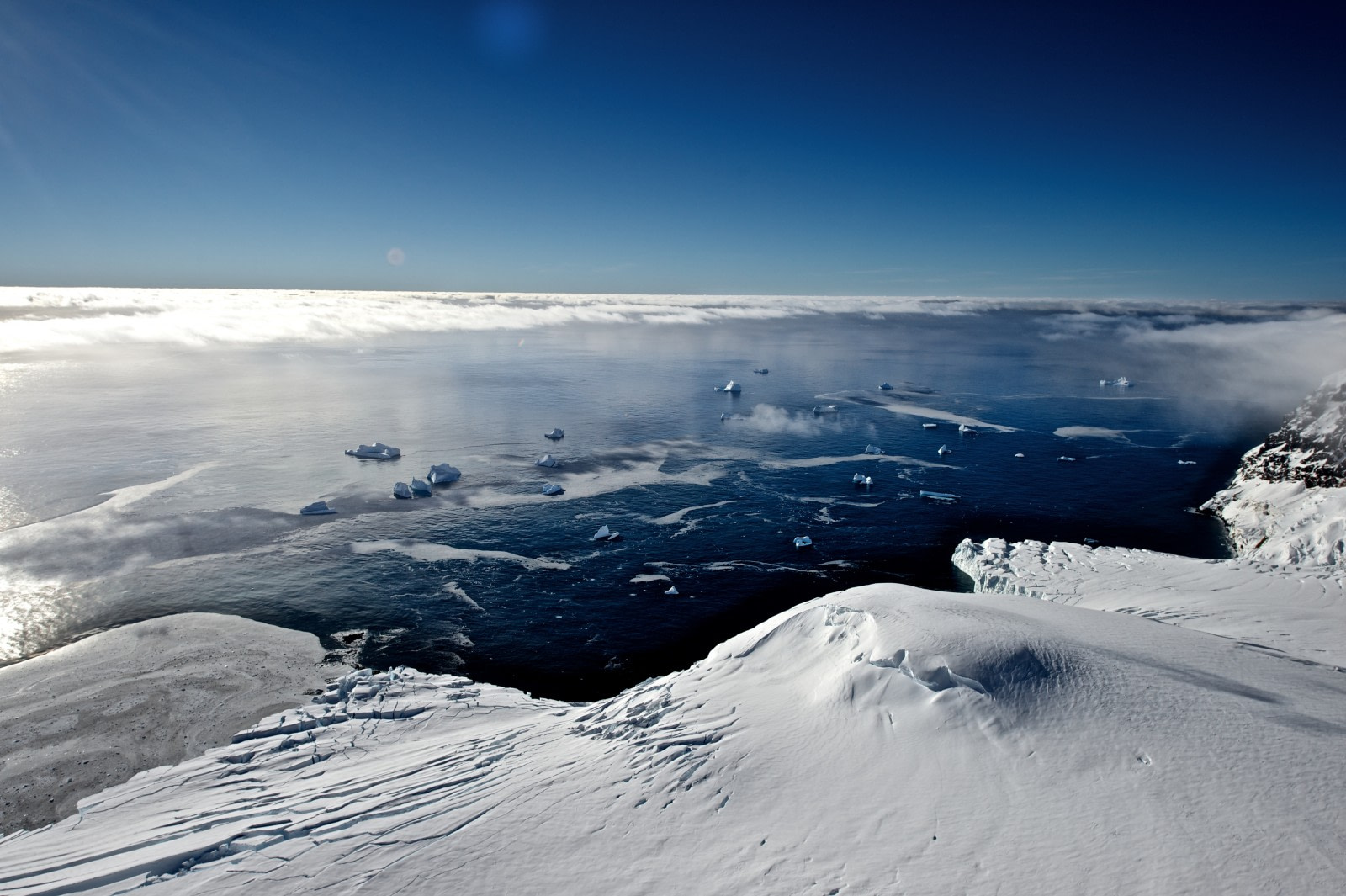
Most of us have at least a vague notion of what makes the North and South Poles so brutally, bone-chillingly cold: They receive less sunlight than the rest of the planet, what sunlight they do receive arrives at an angle, and they’re usually buried under endless mounds of ice and snow. This holds especially true for the South Pole and its centerpiece, Antarctica. Fewer people know, however, what drives Antarctic weather, or what results from it. Here are ten weather-related facts about the most southern continent that will put your polar meteorology ahead of the curve.
1. Antarctica is colder than the Arctic
The Antarctic is in fact the coldest location on Earth. This owes partly to the enormous, and enormously thick, ice sheet that covers about 98% of the continent. But that’s not the only reason: Antarctica also has stronger winds than the Arctic (or any other location on the planet), is surrounded by water (which holds its temperature longer than land), and has the highest average elevation of any continent (4,892 meters, or 8,200 feet). All of these factors combine to keep Antarctica’s average coastal weather around -10°C (14°F) and its inland around -55°C (-67°F). Naturally, the coldest weather recorded on Earth occurred in Antarctica: -89.2°C (-128.6°F) on July 21st, 1983.

2. It was once warm in Antarctica
Despite how frigid the Antarctic is now, it was once as warm as the sun-soaked beaches of California. Studies at Yale suggest that some 40-50 million years ago, during the Eocene epoch, high atmospheric levels of CO2 created greenhouse-like conditions on Earth. Antarctica’s weather at that time averaged 14°C (57°F), with a high of 17°C (63°F), conditions that would quickly reduce the current Antarctic’s titanic icebergs and mountainous glaciers to common ocean swell.

3. Even at its hottest, Antarctica keeps its cool
Since the Eocene, Antarctic weather tends toward the colder side. Even the most boiling temperature recorded in Antarctica was, by most standards, similar to a pleasant autumn day in the Pacific Northwest: At Esperanza Base, an Argentine research station sometimes visited on Antarctic Peninsula voyages, the temperature once reached 17.5°C (63.5°F) on March 24th, 2015.

4. Antarctica is technically a desert – Earth’s largest
Due to the fact that Antarctica receives so little rainfall – the interior averages about 50 ml per year (two inches), usually as snow – it is recognized as a desert. But when Antarctica does something, it does it big: Antarctica is by far the largest desert on Earth, capable of encompassing the Gobi, Arabian, even the sprawling Sahara within its 14.2 million square km (5.5 million square miles). Think of that the next time you watch Lawrence of Arabia.
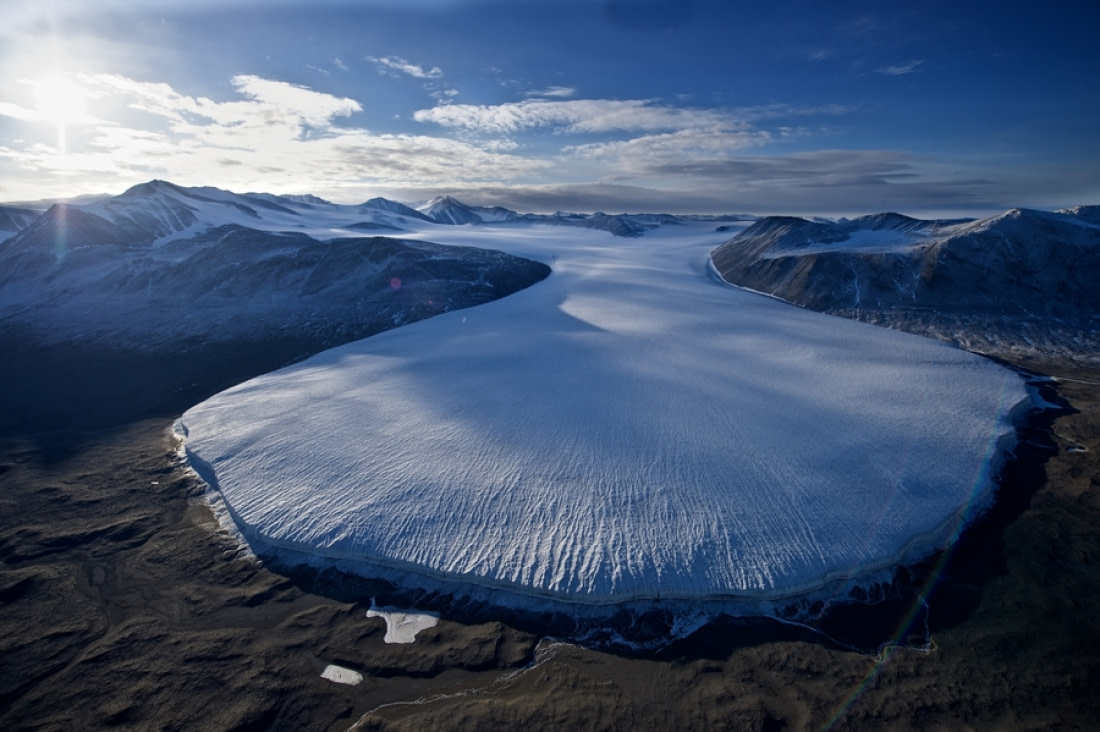

5. Antarctica is almost entirely covered in ice
As mentioned before, some of Antarctica’s cold weather comes from the giant ice sheet covering most of the continent. This large ice sheet is actually two smaller sheets: The West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is the smaller portion, and the East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) is the larger – though for the clarity of this article, we’ll refer to them as one. In total, the Antarctic ice sheet is made up of about 26.5 million square km of ice (6,400,000 square miles) and holds around 61% of the Earth’s fresh water supply. If the ice sheet melted, sea levels would rise roughly 58 meters (190 feet), enough to submerge many of the world’s lowest-lying cities.

6. The Antarctic ice sheet is over 40 million years old
The longstanding cold weather in Antarctica has kept its ice sheet intact for timespans beyond human comprehension. After the Antarctic’s boardwalk-like Eocene weather cooled with the dropping of global carbon dioxide levels, the continent began to glaciate. This icing was aided by a period during which Earth’s orbit led to colder summers, as well as other potential factors, though it was the plummeting CO2 that contributed most directly to the formation and retention of the ice sheet. We can certainly guess, without need of much scientific background, how cold the Antarctic weather was by seeing how sizable that ice sheet eventually became.
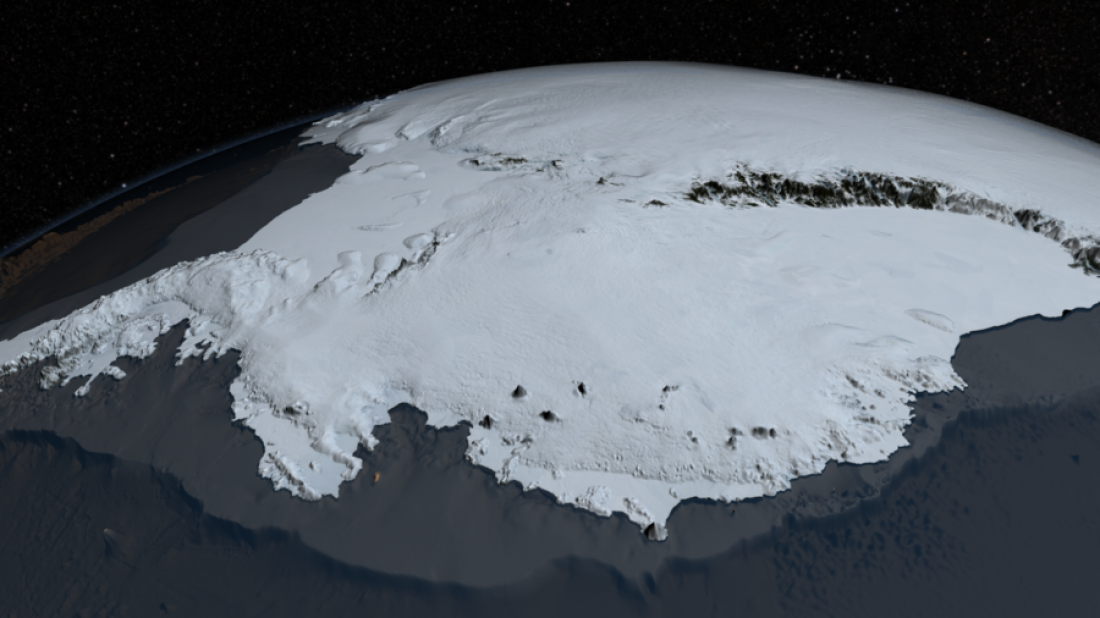
7. Antarctica’s ice averages 2 km thick (over a mile)
A walk of this distance might be no big matter, but a dig… Much different story. Some of the highest elevations on Earth are found in the Antarctic, due partially to the fact that most of its exceedingly thick ice sheet has formed over terrain that was well above sea level already. The resulting ice formations, lofty and surreal, are naturally a chief attraction during Antarctica cruises. The ice sheet itself was not only directly caused by Antarctica’s long history of freezing weather, but eventually became partially responsible for it – and other factors, as we will learn.
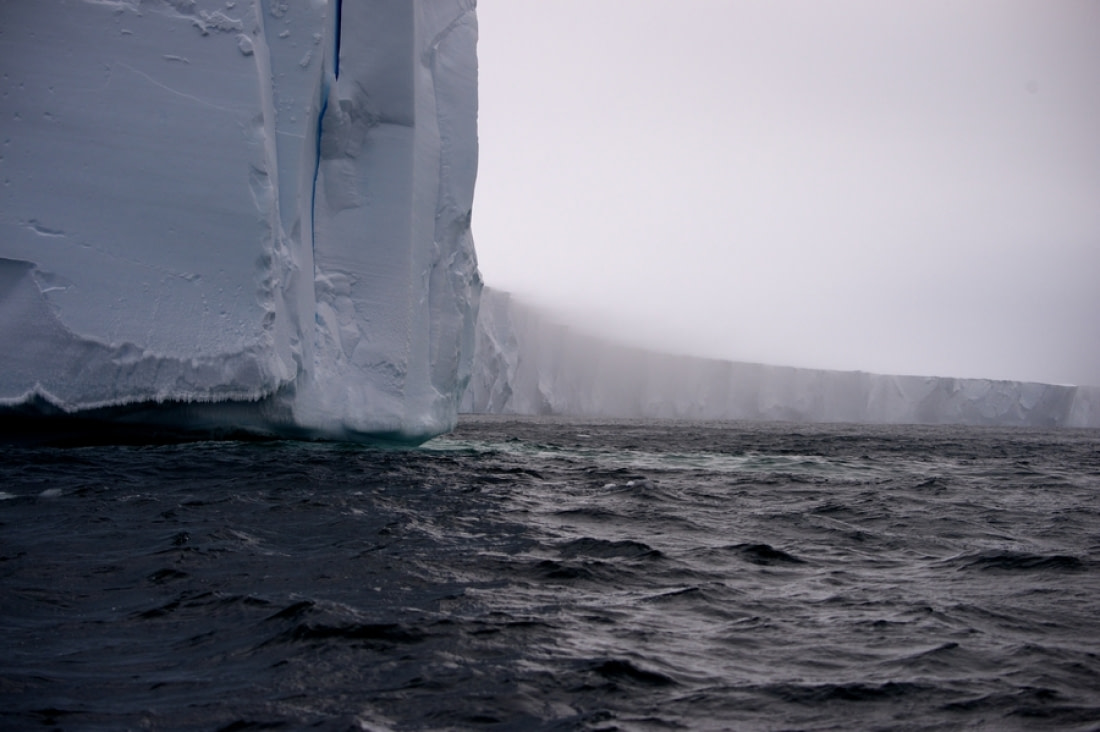

8. Earth’s largest iceberg comes from Antarctica
It should come as no surprise, then, that the continent with the coldest weather, and hence Earth’s largest supply of ice, also produced Earth’s largest-known iceberg. Iceberg B-15, which broke away from the Ross Ice Shelf in late March of 2000, had a surface area of roughly 295 km (183 miles), making it larger than Jamaica and nearly the size of Connecticut. At its largest, B-15 once measured 37 km wide (23 miles) and 295 km long (183 miles). But over the ensuing years, it broke up into smaller pieces, the largest of which drifted north and fragmented in late 2005.
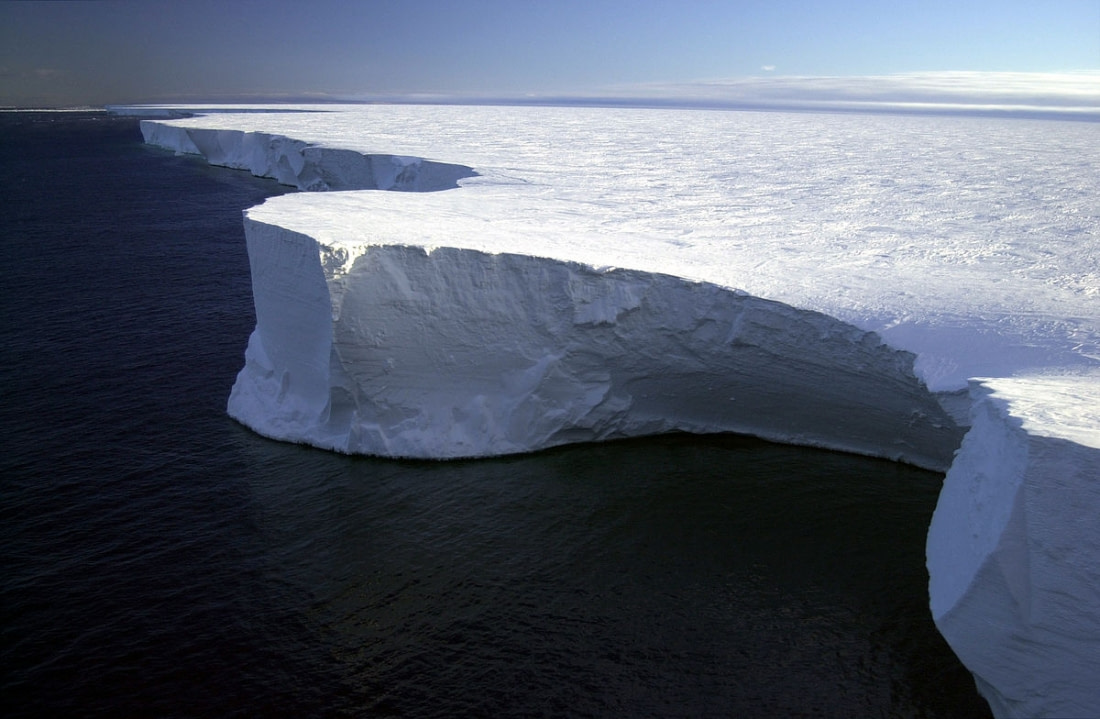

9. Antarctic winds can move at speeds of 320 kph (200 mph)
One of the contributors to Antarctica’s weather is its strong, cold wind. There is in fact a name for the type of wind for which Antarctica is known: katabatic wind, rooted in the Greek word katabasis, or “descending.” Also called “fall winds,” these gravity-driven gusts push high-density air downward from above high-altitude slopes. Most of this wind usually only reaches speeds of around 18 kph (11 mph), but over the Antarctic’s enormous ice sheets, large concentrations of cold air build up over time and shove downward with considerable force. When that wind is funneled through narrower areas along Antarctica’s coast, for example, it can blow at hurricane speeds.

10. Antarctic ice melting has caused a gravity shift
Global warming no doubt has more surprises in store for us, but one of them was recently revealed when scientists discovered that the melting of Antarctica’s ice is actually weakening gravitational pull in that region. Gravity on Earth’s surface, far from a constant, varies slightly by location and is largely dependent on geological factors: the rotation of the planet, the position of ocean trenches and mountain ranges, and the presence of large masses of ice. When that ice is reduced in a given location, so too is the power of gravity in that location. The decreasing ice in Antarctica is having exactly this effect, a rather unexpected chapter in a continuing story.

Blog



5 Life Lessons You'll Learn in Antarctica

Six Facts About the Crabeater Seals of Antarctica

Arctic Seals

Under the Greenland Ice Sheet

Amphibian, reptiles and herbivore mammals in the Arctic

Flowers in Antarctica

Camping in Antarctica: a True Expedition Experience

The Northern Lights dancing across the skies

Birding Opportunities Abound in Spitsbergen

The Ins, Outs, and Ups of Polar Mountaineering & Ski Mountaineering

Guidelines for visitors to Antarctica

Antarctica’s first Marine Protected Area

The Eight Great Penguin Species of Antarctica

How Arctic Wildlife Differs from Antarctic

A Diving Dream Fulfilled

Antarctica Cities (and Five Other Things That Don’t Exist There)

The Secret Life of Glaciers: How They Form, Move, and Melt

Humpback Whales: the Stars of the Western Antarctic Peninsula

10 Popular Bird Watching Binoculars