Whales are the world’s largest mammals, found in the Arctic and Antarctica. This article covers some of the major species you may see on voyages to these remarkable areas.
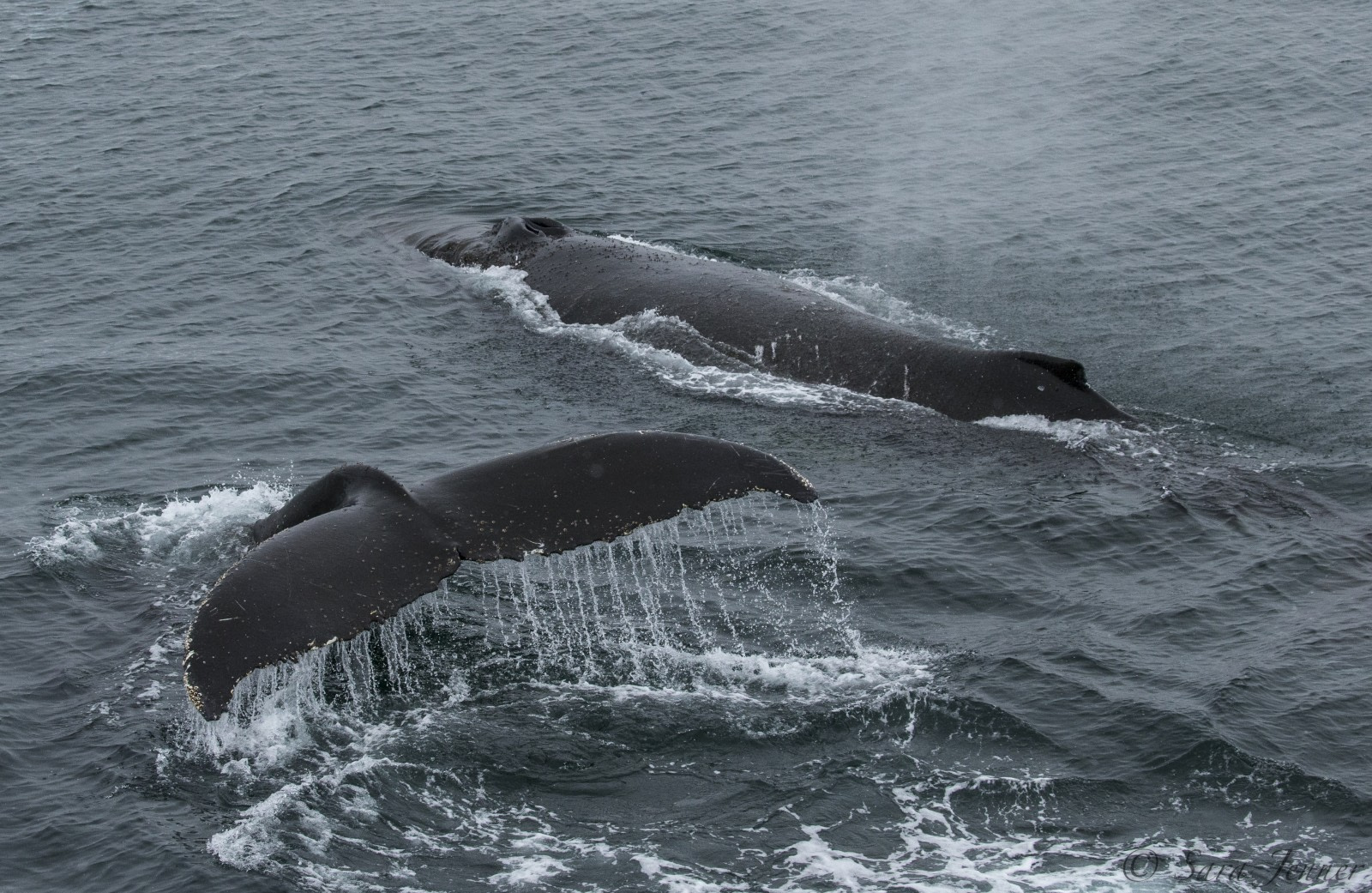
Humpback whales commuting to warmer waters
The humpback whale has a small dorsal fin with a distinctive hump at the front. Their tails have a unique black and white pattern, enabling individuals to be identified. These whales are one of the most active whale species, with behaviour that includes breaching, slapping their tales and fins on the water surface, and competing with one another (among males) for mates in breeding grounds.
Humpback whales communicate with one another through their famous songs, which are different in breeding versus feeding areas. The song is usually less than 10 minutes long and can be repeated many times, even for hours without stopping.
Humpback whales undertake seasons-long migrations that can be up to 10,000 km (6,213 miles) per year, travelling between the summer feeding grounds, where you would see them during an Antarctica trip, and their winter calving/ breeding grounds in tropical waters.
Humpbacks are baleen feeders and have a general diet that consists of krill and small schooling fish, including mackerel and herring. Their feeding techniques include lunging through groups of prey and stunning prey with their flippers.

Minke whales gulping large portions of food
Minke whales are found in Antarctic waters, including areas of heavy pack ice, during the middle of winter. During the summertime, their favourite place appears to be open pack ice, which is pack ice with a lot of open water among the ice floes. When the ice is thick, the minke whale breathes by sticking its pointed head up through narrow cracks in the ice.
Minke whales are fast swimmers, often breaching the surface. They can stay underwater for as long as 20 minutes. Minke whales feed almost entirely on Antarctic krill, feeding in groups that can number in the hundreds when there are abundant supplies of food.
Scientists have found that minke whales can gulp mouthfuls of krill nearly every 30 seconds, making them one of the fastest filter-feeding whales. Using tracking data from tags, researchers found that minke whales skim the underside of the ice, gulping krill as they swim. Minke whales used this technique up to 24 times per dive.

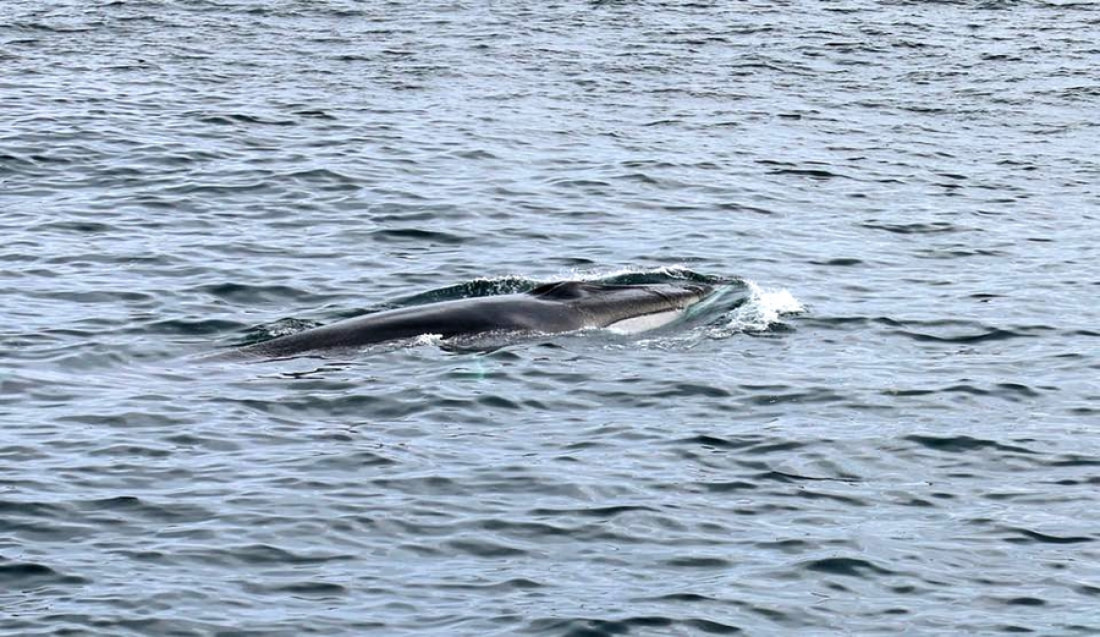
Sei whales skimming food from the water
The sei whale is a uniformly-coloured whale with soft, swirling marks on its skin. These whales are the fastest swimming baleen whales, having been recorded reaching speeds of up to 25 kph (15 mph).
Sei whales appear not to form any long-lasting family groups and are usually seen in groups of less than five. They are the most northern Antarctic baleen whale, often found north of the polar front in summer.
There is little known about sei whale winter breeding, but what is known is that pregnancy lasts 11.5 months and a single calf is born in the winter. The calf is suckled around seven months before it becomes independent of its mother.
Sei whales are the only member of the roqual family that feed on small copepod crustaceans instead of the larger krill. Their feeding method is different to the other whales: instead of gulping their food, sei whales skim it by swimming along the water with their mouths wide open.
The fin whale’s hunting face
Fin whales are the second-largest living mammals, blue whales being the largest. Fins tie blue whales for making the lowest-frequency sounds of any animals. The fin whale got the nickname “Razorback” thanks to a pronounced ridge seen behind their dorsal (top) fin.
They have a unique asymmetrical colourization feature on their faces: The right underside of their jaw, right lip, and the right side of their baleen are a yellowish-white, while the left-side correspondents are gray. Some scientists think the colouring comes from hunting – the whales keep the white side towards school of fish while forcing them into a ball, presenting a more threatening aspect.
But because fin whales are mostly pelagic (spending most of their time out in deep seas away from coasts), they are hard for scientists to study. When fin whale sounds were first recorded, scientists in fact thought that they were geological sounds (like tectonic plates grinding).
A fin whale in the wild can live to be 90 years old. Females can reach sexual maturity starting at 6 years old. They give birth every 3 to 4 years, and the pregnancy lasts close to one full year.
Like other baleen whales, fin whales open their mouths to swallow huge amounts of water. They then close their mouths and force the water back out through their baleens, trapping their prey. Fin whales can sustain speeds of around 35 kph (22 mph). While feeding, they swim around 10 kph (6 mph), but they can burst up to 45 kph (28 mph).

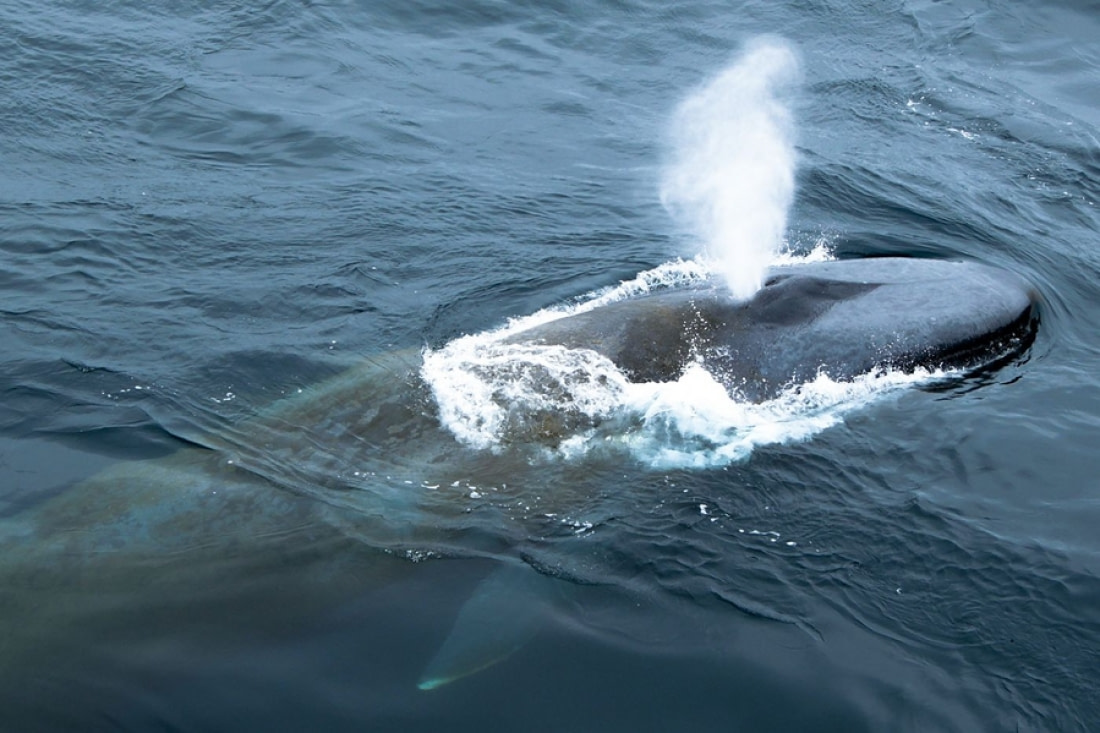
Sperm whales in nursery or bachelor schools
The sperm whale has wrinkly skin and a large, square head that makes up a third of its body length. It has a purply-brown or dark-grey colour and is white underneath. Sperm whales are typically uniform in color, with variations around the jaw and genital regions.
They are found throughout the world, so you can see them in Antarctica as well as in the Arctic. Sperm whales prefer deep waters of more than 200 metres (656 feet) and are usually found offshore and in areas with submarine canyons.
They are toothed whales and take deep dives to catch their prey, which includes squids. Males often hunt for larger prey, including sharks and rays. Scientists believe sperm whales feed using clicks that can locate as well as stun their prey.
They are known to take dives that last longer than one hour and reach depths of more than 1,000 metres (3,280 feet). However, the typical sperm whale dive lasts around 35 minutes and reaches depths of 400 metres (1,312 feet).
Throughout their lives, sperm whales are either in “nursery schools,” which are adult females with young, or “bachelor schools,” which include males between seven and 27 years of age.
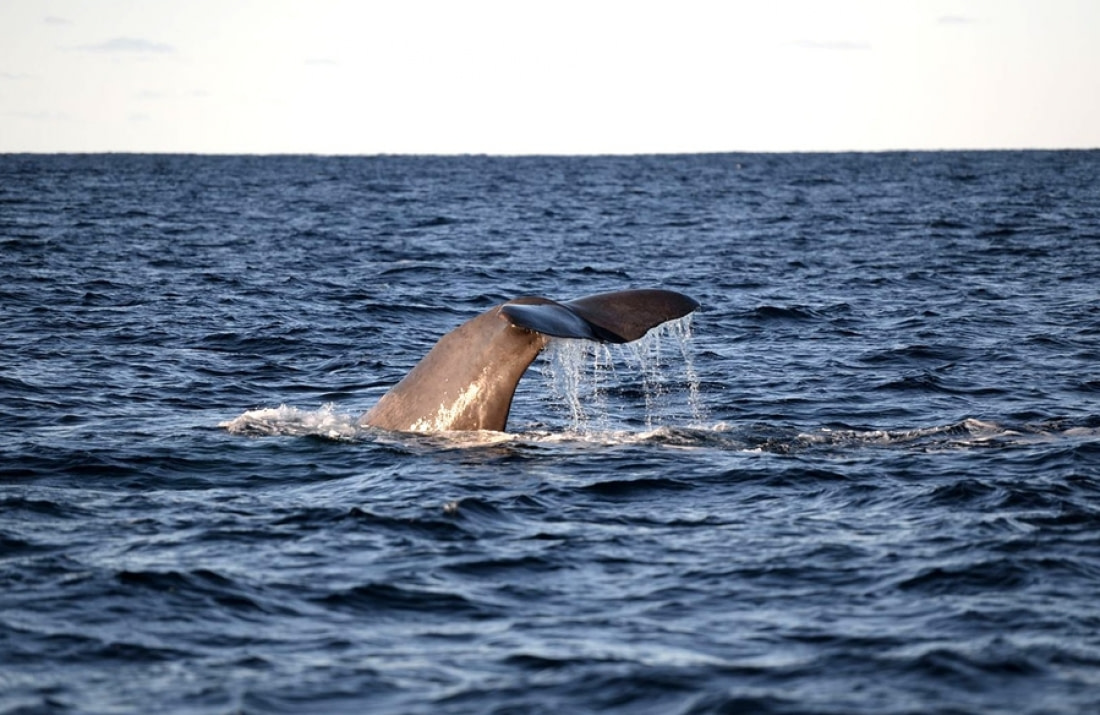

Narwhals stunning their prey
Narwhals spend their time in Arctic waters. Though not among the more common whales seen, you would most likely encounter them during Svalbard or Greenland voyages. They can also be found around Canada and Russia. While they cannot be completely accurate, scientists believe that 90 percent of the narwhal species population is found in Baffin Bay, located between western Greenland and Canada.
The narwhal is known for its long tusk that spirals counter-clockwise several feet from its upper lip. This tusk is in fact the whale’s upper canine tooth, and some males having two of them. However, only around 15 percent of narwhal females have one. Scientists have captured video of narwhals using their tusks to stun Arctic cod, immobilising them and making them easier to catch. The tusk also provides the narwhal sensory capabilities, as it has up to 10 million nerve endings inside.
Beluga whales singing in the seas
Beluga whales are a social species that lives, hunts, and migrates together in pods that can number around a few hundred. They have a melon-shaped forehead, can make facial expressions, and also can produce chirps, clicks, whistles, and squeals. These noises have led to whale’s reputation as the “canary of the sea.”
Most populations of beluga migrate, moving south in autumn as ice forms in the Arctic. In spring, when the ice breaks up, beluga whales return north to their feeding areas. Over the summer period, beluga whales are often found near river mouths and even venture upstream. One beluga whale was recorded swimming 1,000 km (621 miles) inland up the Yukon River.
Beluga whales usually feed in open water as well as in benthic habitats in various depths of water, and one was recorded as diving to more than 350 metres (1,148 feet) to feed. These whales eat a variety of food, including salmon, herring, shrimp, Arctic cod, flounder, crabs, and molluscs.
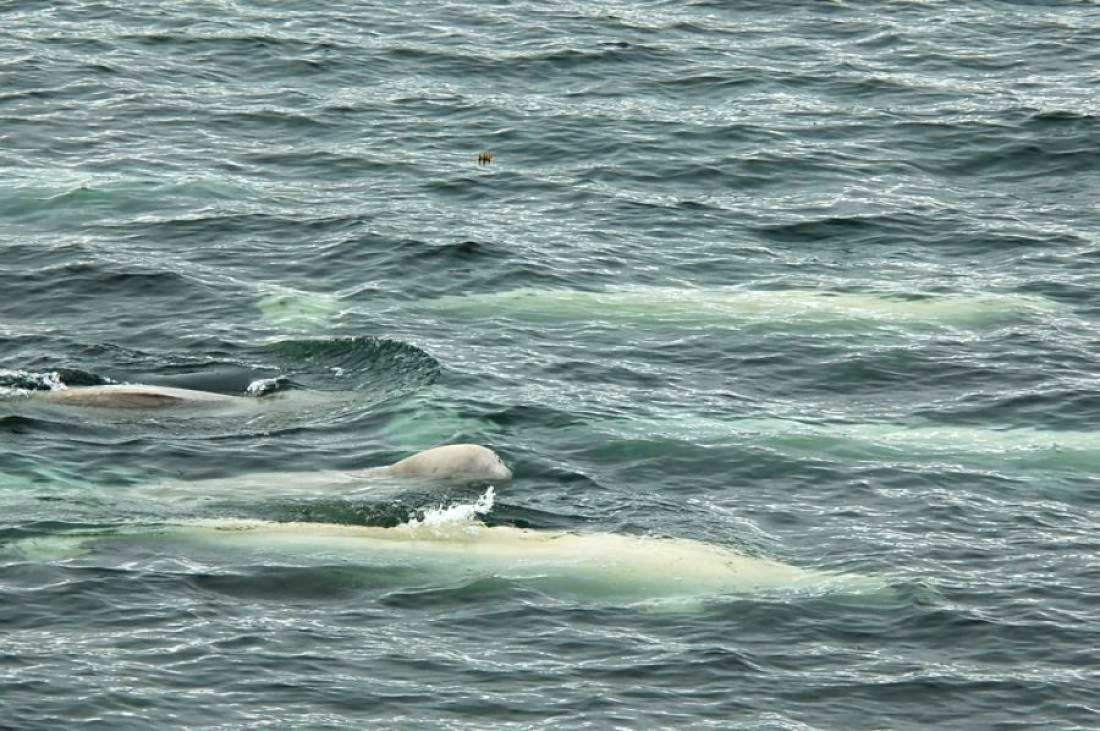

Bowhead whales breaking the ice
The bowhead whale is a predominantly Arctic species, its movement influenced by ice melting and freezing. The whale has a one-of-a-kind double-humped profile and lacks a dorsal fin. Bowhead whale heads comprise one-third of their total body length and have two blowholes.
The bowhead whale usually feeds on the surface or just below it, using the skim-feeding method. While there is little known about the bowhead whale’s diving habits, scientists believe it can dive to depths of more than 200 metres (656 feet), with an average dive time ranging from four to twenty minutes.
There has also been recorded accounts of these whales diving for over an hour at a time, resurfacing in the same place. When bowhead whales rise to the surface, they can break ice that is up to 60 cm thick (23 inches) to make a breathing hole.
Bowhead whales usually travel in groups of three or less, but they typically congregate in larger numbers in feeding grounds.
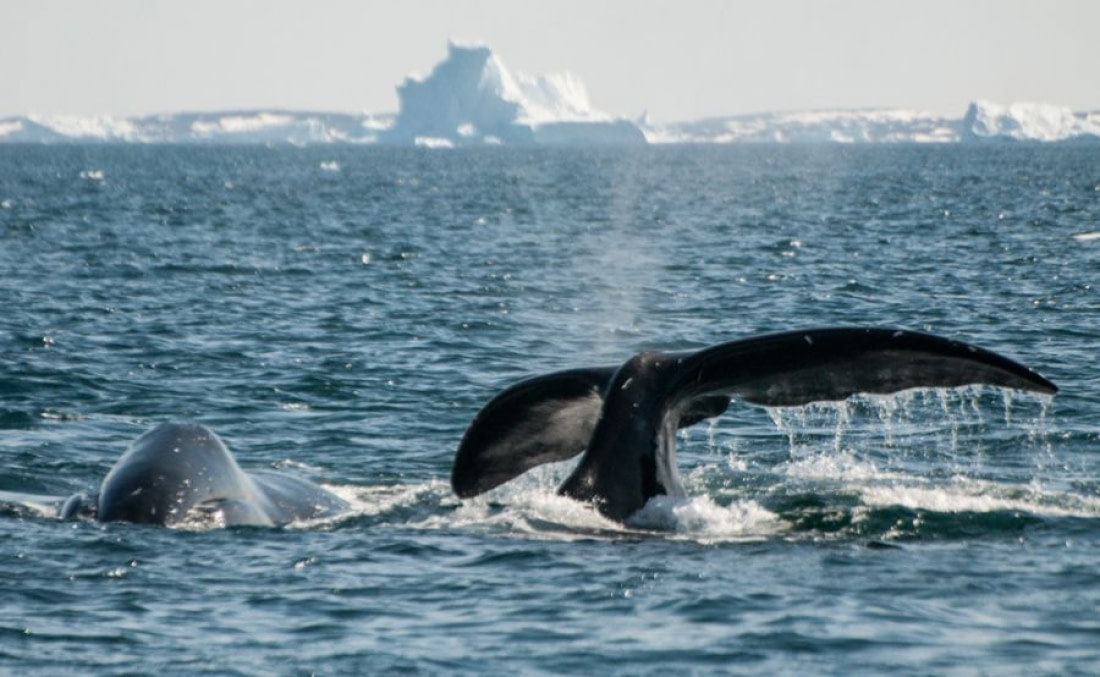

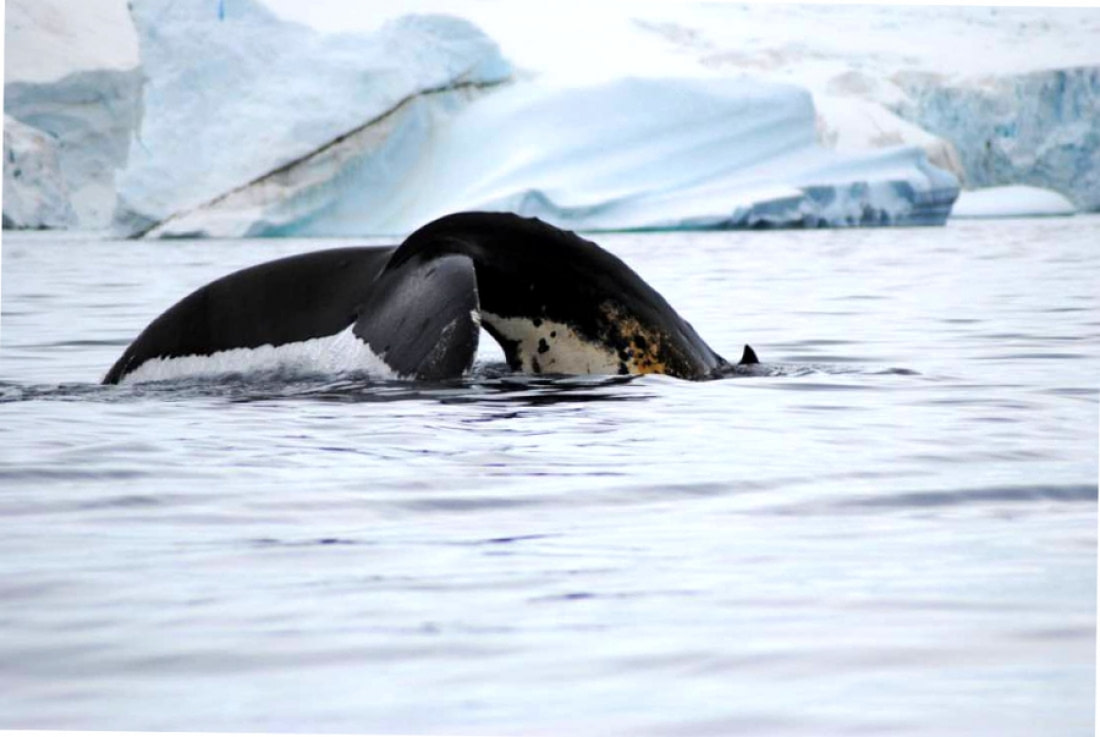
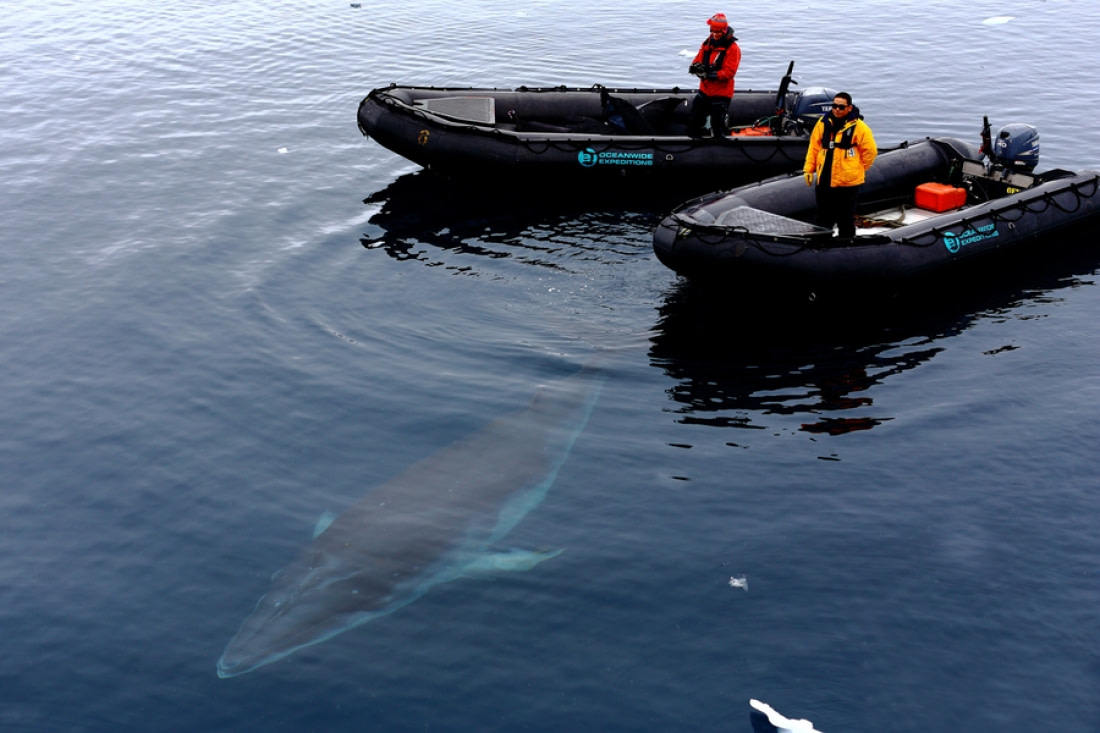
Blue whales, the titans of the ocean
The largest species Earth has yet created, the blue whale, grows to around 30 metres (98 feet) in length. Though blue whales have not recovered from the great whale hunts of the early 20th century, they may sometimes be spotted in Antarctica’s open waters. Blue whales are one of the world’s longest-living species: The oldest whale is thought to have lived to 110 years old, while the average blue whale lifespan is upwards of 80 years.
During the summer months, blue whales often swim near the edge of the Antarctic sea ice. These whales look blue underwater, but on the surface they are more of a mottled blue-grey. Blue whales feed nearly exclusively on Antarctic krill, and adults are able to consume around 4 tonnes (8,800 pounds) of krill per day.
Blue whales can be found in small groups, but typically they swim alone or in pairs. They often swim around 8 kph (5 mph) but can race up to 32 kph (20 mph) when necessary. Underwater the whales are very loud: Their pulses, groans, and moans able to be detected by other blue whales up to 1,600 km (1,000 miles) away.
Baby blue whales are born weighing up to 3 tonnes (6,600 pounds) and measuring 7.6 metres (25 feet) in length. Feeding off their mother’s milk, baby blue whales put on 90 kg (200 pounds) each day in the first year alone.

Blog



The Return to Franz Josef Land

Albatross, penguin and krill research in Antarctica

5 Life Lessons You'll Learn in Antarctica

What’s so Special about East Spitsbergen?

Antarctica’s first Marine Protected Area

Gough Island: Seabird Capital of the South Atlantic

Kayaking In Greenland

10 Traits of Post-Ice-Age Greenland

Birding Opportunities Abound in Spitsbergen

Everything you need to know about Antarctic icebergs

Arctic Seals

Get to Know Your Ice

10 Bountiful Blue Whale Facts

The Arctic Hare: Easter Bunny

Svalbard’s 12 Most Iconic Animals

Weddell seals: The data collectors scientists of Antarctica

10 Tried-and-True Bird Photography Tips

Six Seal Species You Might See On Your Greenland Cruise

10 Popular Bird Watching Binoculars