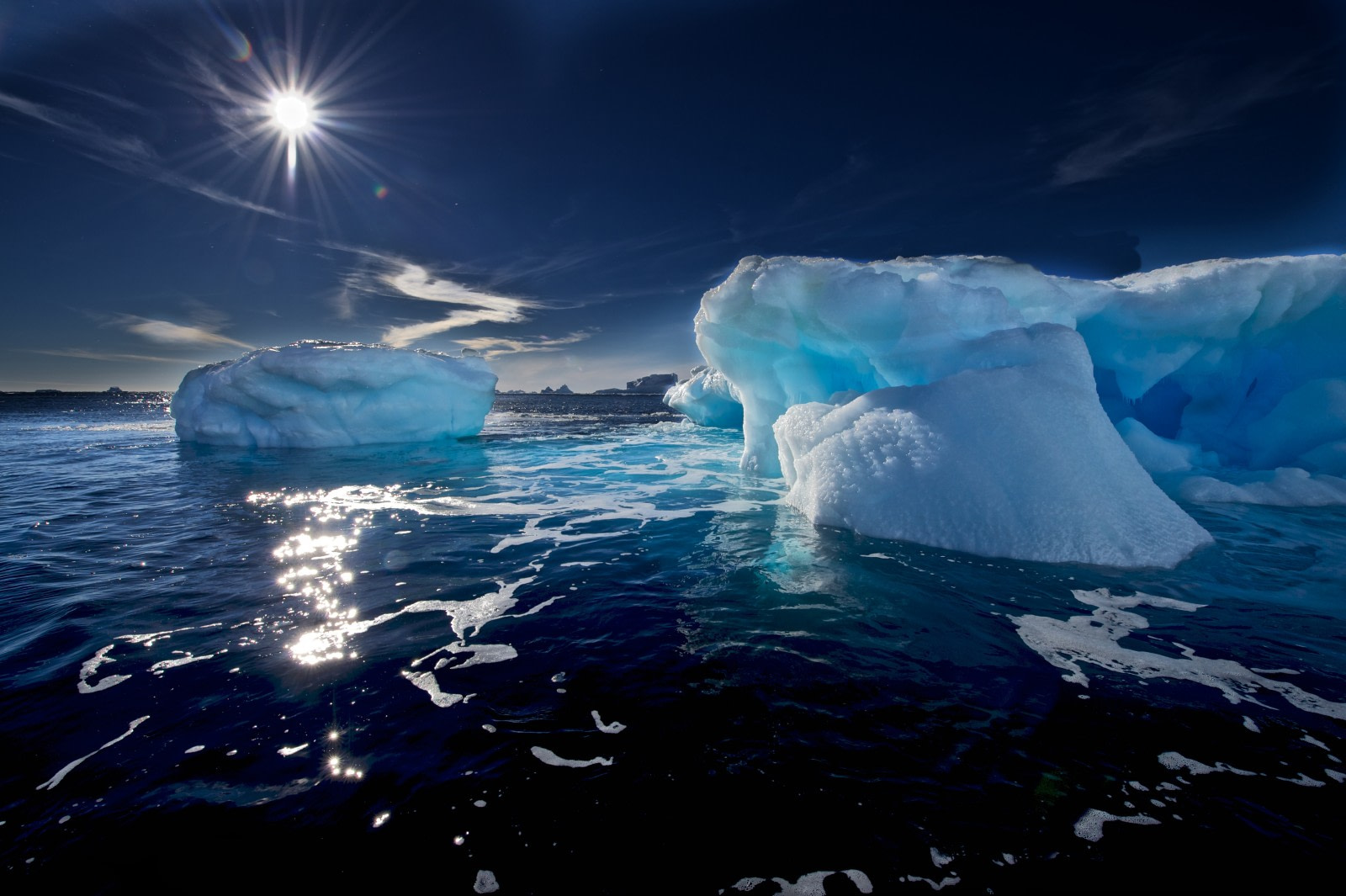
The ice in Antarctica might seem static, but it is constantly moving. Pieces of ice are continuously breaking off from ice shelves, glaciers, or other icebergs. They float freely along with the Antarctic currents, with about 90 percent of their mass below the surface of the water. This fact is actually what gave rise to the nowadays popular phrase “the tip of the iceberg”. Regardless, the sighting of the first iceberg is always a moment to celebrate in any and all Antarctic expeditions. So that you may appropriately ready yourself for that joyous moment, in this article you will find everything you need to know about Antarctic icebergs.
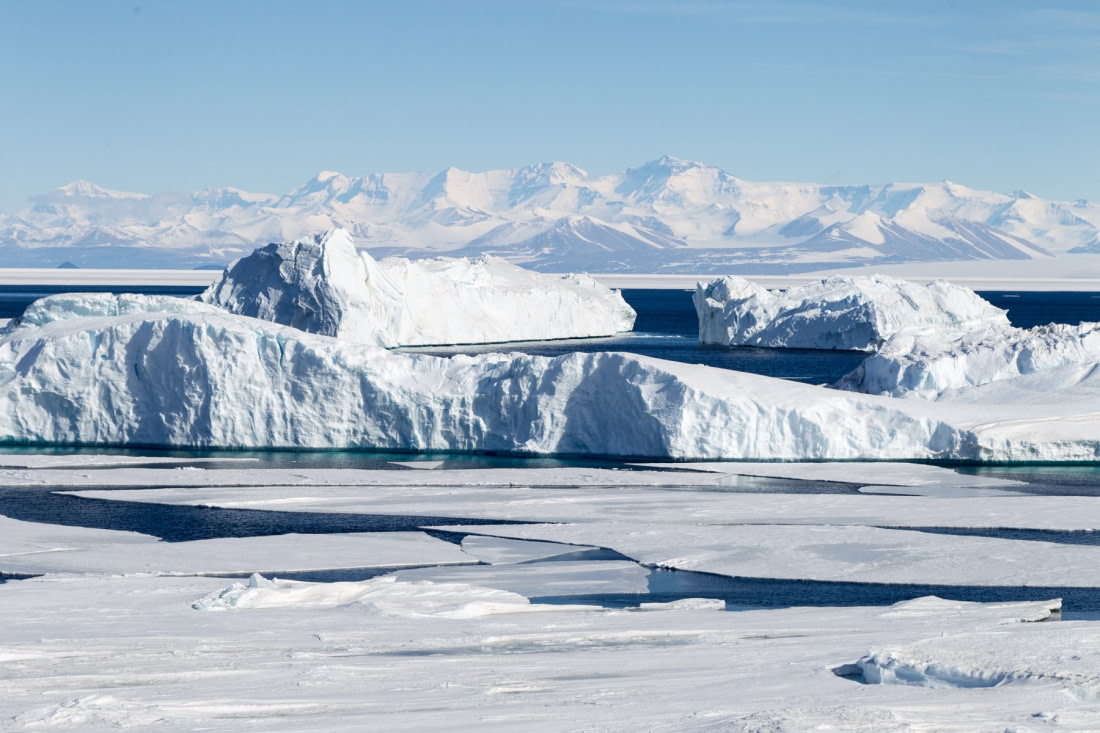

Types of icebergs
When one imagines icebergs, the first image that usually comes to mind is that of an immense spiky iceberg, majestically floating in the freezing waters. But in reality, any chunk of ice larger than 5 meters (16 feet) across and at least 30 meters (98 feet) thick can be called an iceberg -- and they come in various sizes and shapes to boot. Typically, they are divided into two main categories, tabular and non-tabular icebergs.
Tabular icebergs
Tabular icebergs have steep sides and a flat top, much like a plateau. This type of iceberg can be quite large, and it can sometimes be referred to as an ice island, such as in the case of the Pobeda Ice Island.
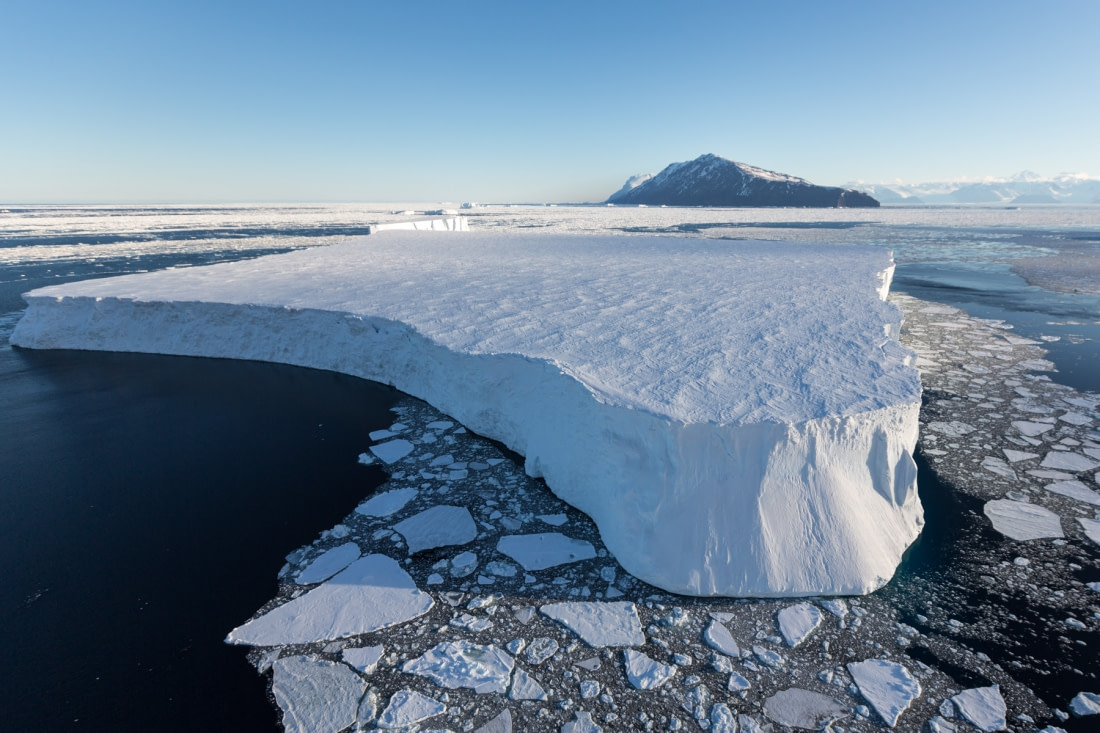

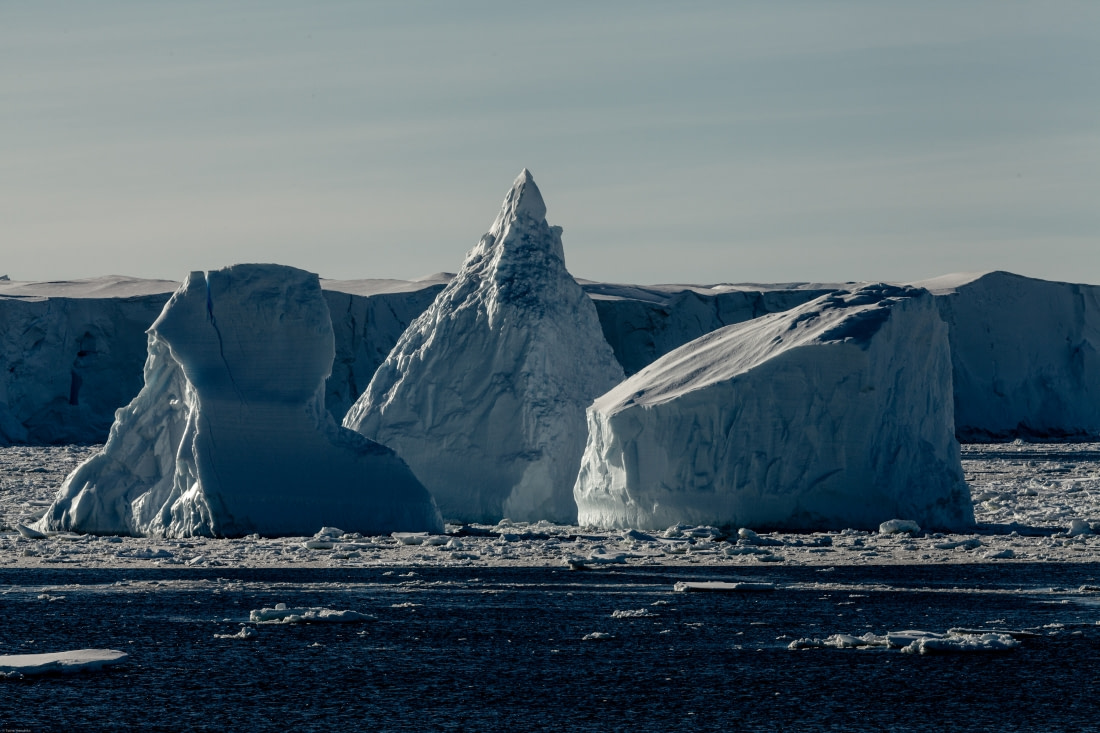
Non-tabular icebergs
Non-tabular icebergs have different shapes. The following are some common types of icebergs and the names used to describe them in iceberg observation.
- Dome: An iceberg with, of course, a rounded top.
- Pinnacle: An iceberg with one or more spires.
- Wedge: An iceberg with a steep edge on one side and a slope on the opposite side, the top is shaped into a pyramid-like tip.
- Dry-dock: An iceberg that has eroded to form a little U-shaped harbor-like enclosure.
- Blocky: An iceberg with steep, vertical sides and a flat top. It differs from tabular icebergs in that its shape resembles more a block rather than a flat sheet of ice.

Smaller pieces of floating ice are known as bergy bits and growlers. Bergy bits and growlers can originate from glaciers or shelf ice, and may also be the result of a large iceberg that has broken up. A bergy bit is a medium-to-large fragment of ice about the size of a small house. Its height is generally greater than three feet, but less than 5 meters (16 feet) above sea level. Growlers are smaller fragments of ice that extend less than 1 meter (three feet) above the sea surface and measure about the size of a grand piano. They are often transparent but can appear green or black in color.
Tracking and naming icebergs
The icy waters surrounding Antarctica are home to a vast majority of the icebergs that navigate Earth’s oceans. Icebergs are monitored worldwide by the U.S. National Ice Center (USNIC), which is the only organization that names and tracks all Antarctic icebergs larger than 1650 meters (5,400 square feet). They provide global ice analyses and forecasts, and more than 95% of the data used in its sea ice analyses are derived from the remote sensors on polar-orbiting satellites. This information is invaluable for scientists who study icebergs. Due to the work of the USNIC, scientists are able to learn more about climate and ocean processes and ships traversing the Antarctic waters are informed of any icebergs which might pose a danger along their journey. Iceberg names are derived from the Antarctic quadrant in which they were originally sighted. The quadrants are divided counter-clockwise in the following manner:
A = 0-90W (Bellingshausen/Weddell Sea)
B = 90W-180 (Amundsen/Eastern Ross Sea)
C = 180-90E (Western Ross Sea/Wilkesland)
D = 90E-0 (Amery/Eastern Weddell Sea)
On October 22nd, 2015, the USNIC discovered a new iceberg using satellite imagery. This particular iceberg calved from iceberg B-09B, which had been grounded near the new iceberg’s present position since 1993. B-09I is located at 66°35’ South, 142°23’ East in the Wilkesland Sea, and measures 14 nautical miles on its longest axis and 6 nautical miles on its widest axis.
Iceberg detection
Icebergs can be detected in the open sea both visually and by radar. In principle, an iceberg can also be detected by sonar. In the open sea, an iceberg produces squealing, popping, and creaking sounds caused by mechanical stress and cracking; and these sounds can be detected underwater up to 2 km (more than one mile) away. During the summer, ‘bergs can also produce a high-pitched hissing sound called a “bergy seltzer,” which is due to the release of high-pressure air bubbles from the ice as it melts in the warmer water. In the past, iceberg positions were sighted by ships or aircraft; however, it is becoming more common for icebergs to be sighted using satellite imagery. The most useful type of sensor is the high-resolution synthetic aperture radar (SAR), that is able to detect icebergs day or night, independent of the weather conditions. When necessary, icebergs are captured and towed out of the way of their targets.
Iceberg drift trajectories
A freshly calved iceberg usually begins by moving westward, along with the Antarctic Coastal Current, with the coastline on being on its left-hand side. The Coriolis force owing to Earth’s rotation also turns its trajectory to the left, which cause the icebergs to run aground and remain stationary for years before continuing on their journey. If a ‘berg can break away from the coastal current, it then enters the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, or West Wind Drift. This eastward-flowing system circles the globe at latitudes of 40°–60° S. Icebergs tend to enter this current system at four well-defined longitudes or so-called “retroflection zones”: the Weddell Sea, east of the Kerguelen Plateau at longitude 90° E, west of the Balleny Islands at longitude 150° E, and in the northeastern Ross Sea. Once the iceberg is in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, its path is generally eastward, driven by both the current and the wind. Also, the Coriolis force pushes the ‘berg slightly northward. The ‘berg will then move crabwise in a northeasterly direction, finishing its days at relatively low latitudes and in relatively warm waters before disintegrating. Under extreme conditions, an iceberg may succeed in reaching extremely low latitudes. For example, clusters of bergs with about 100 feet of freeboard were sighted in the South Atlantic at 35°50' S, 18°05' E in 1828. Today, iceberg trajectories are predicted by increasingly sophisticated computer models.
Blog



10 Bountiful Blue Whale Facts

9 Facts about the Greenland Shark

Eight Engaging Reindeer Facts

5 Life Lessons You'll Learn in Antarctica

Graham Land: A landscape dominated by volcanoes

The Ins, Outs, and Ups of Polar Mountaineering & Ski Mountaineering

The Classic Polar Cruise: Antarctic Peninsula Facts, Pics, and More

Adding Antarctica to Your Seven-Continents Bucket List

Seven Tips to Get the Most out of Your Expedition Cruise

Greenlandic Inuit Beliefs

8 Scientific Wonders of the Arctic

Solargraphy & Pin Hole photography in the Arctic

Path of Polar Heroes: Hiking Shackleton’s Historic Route

Antarctic Explorer’s Voyage

South Georgia Whaling Stations

Ice streams and lakes under the Greenland Ice Sheet

Arctic on Foot: Hiking and Snowshoeing the Far North

Amphibian, reptiles and herbivore mammals in the Arctic

Antarctica in Pictures: Photos from 2018