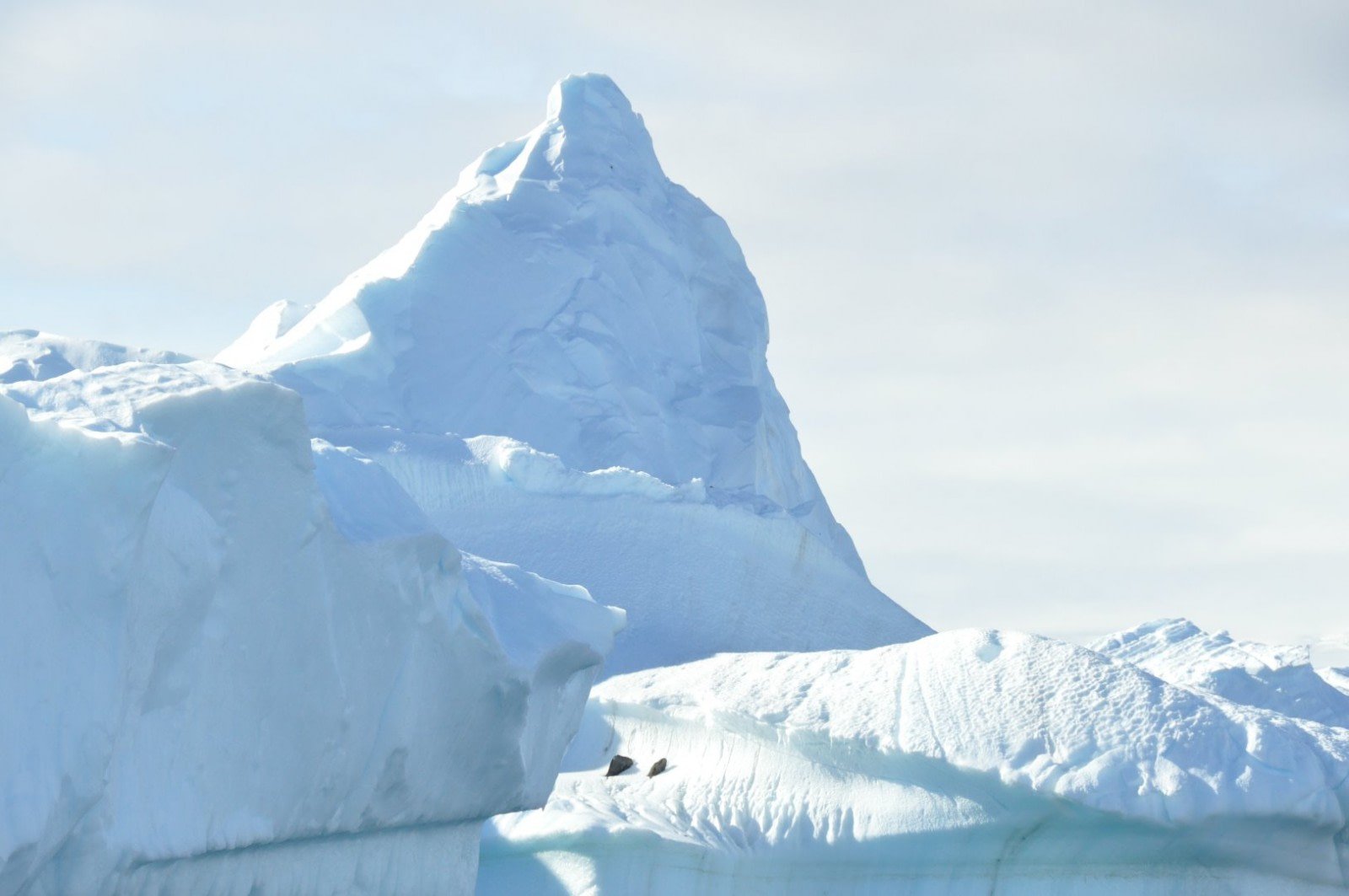
Since James Cook’s second voyage to Antarctica from 1772-1775, which provided the first descriptions of Antarctic animals, scientists have progressively uncovered the biodiversity of the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic regions. Numerous expeditions and research projects have since been undertaken to understand the unique ecosystems of this continent.
The Polar Front is Permeable
One major area of research is the Polar Front, an oceanographic barrier between the Southern Ocean and its surrounding water masses. Recent discoveries have shown that it is not an impermeable biogeographical barrier as previously thought.
One of the initial studies on the biogeography of the waters above and below the Polar Front was the development of the South Georgia Marine Biodiversity Database (SGMarBase). This database was created to establish a baseline on the various macro- and mega-benthic biodiversity of the South Georgia shelf and slope, enabling scientists to identify key species and biodiversity hotspots. The archipelago of South Georgia is one of the largest, most isolated land masses in the Southern Ocean.
Due to its early separation from a continental land mass, large shelf area, geographical isolation, and proximity to nutrient-rich currents, the area is biologically rich and distinct. The database was the first attempt to map the biogeography of an archipelago south of the Polar Front, incorporating biological data with physical data such as seabed topography and physical oceanography.
Before this database, scientists had collected a large amount of biodiversity data from the area, but it was scattered across numerous literary sources, stored by various institutes, and in different languages. The data was also not logged with georeferences.
By collating, checking, and standardizing this data into one repository, scientists now have access to a central database holding nearly 25,000 records and identifying over 1,400 species from the South Georgian shelf, including sea urchins, free-swimming worms, fish, sea spiders, and crustaceans. This database shows that South Georgia supports more species than the Galapagos and Ecuador combined and hosts the densest mass of marine mammals on Earth during the breeding season.
The Polar Front’s Biodiversity
In a more recent study, scientists have discovered that the Polar Front may be even richer than previously believed. A new study provides the most complete inventory so far on the distribution of bryozoans, marine invertebrates that live in colonies and form mineralized skeletons in the shallow waters of the Falkland Islands and the South Georgia Islands.
In this study, a group of scientists from various institutions, including the Biodiversity Research Institute of the University of Barcelona, British Antarctic Survey, and the South Atlantic Environmental Research Institute, identified 85 different species, among which are 18 types and 23 species that could be unknown. From all the identified species, 65 percent were named for the first time in the Falkland Islands. According to one scientist, the new inventory for bryozoans will enable the creation of a database of regional bryozoan diversity and allow researchers to detect possible invasive species.
Overall, the study, which extends the bathymetric study range into 30 marine species, analyzed the fauna similarities among the communities of bryozoans in neighboring areas and will help design biogeographical distribution patterns. The scientists now state that the Polar Front is not as impermeable as once thought, as they have found evidence of species spreading across the Patagonian region to Antarctica.
How Did Life Spread Throughout the Antarctic Region?
Scientists from Monash University in Australia are leading a terrestrial component of a major new expedition to better understand Antarctic ecosystems. Using new genetic and computational approaches, the team will seek answers to an unresolved question: how has life evolved and spread around the Antarctic region both in the past and today?
The project, named A Functional Biogeography of the Antarctic (AFBA), forms part of the wider Antarctic Circumnavigation Expedition (ACE). ACE involves 22 projects, 55 researchers, and 19 countries and is managed by the Swiss Polar Institute. As part of the Monash University project, scientists from around the world, including France, Germany, New Zealand, Russia, South Africa, the United Kingdom, and the United States, will visit sites across the sub-Antarctic and Antarctica to uncover new species of animals and plants, which will guide new ways to help conserve biodiversity in the Antarctic regions.
Specifically, AFBA will provide a comprehensive biodiversity assessment of the region’s terrestrial and intertidal plants and animals. Based on the assessment of these species with advanced genetic and computing techniques, the researchers will be able to create a biological history of the region, showing where different groups have their origins, how different species across the islands are related and connected, and how life on these islands is related to that of other southern continents.
The researchers will also attempt to understand how frequently different groups have moved between Antarctica and the sub-Antarctic islands, when this happened, and the extent to which it continues today. By genetically testing species found, it will provide insights into the adaptations that have enabled life to flourish in the Antarctic region. Regarding future protection of the continent, the scientists aim to provide a baseline biodiversity surveillance system for the region to help conservation managers identify the species to which newly arrived individuals belong and whether they pose a threat.
The overall aim of AFBA is to leave a legacy for future scientists in several areas, including:
- Resolution of fundamental questions about how life has evolved in Antarctica
- Discovery of species new to science
- Improved understanding of the region to benefit conservation management
- Publicly accessible information to improve knowledge and appreciation of Antarctica’s wilderness, conservation significance, and sheer beauty
- Education and inspiration of a new cohort of polar scientists and enthusiasts
Finding the Connection Between Life on Land and Water
In addition to understanding biodiversity in the waters around the continent, scientists are also trying to understand the link between biodiversity on land and water. For instance, in the Falkland Islands, scientists are learning about its biodiversity and what can be done to preserve it for future generations. In one study, researchers from the University of Maine studied the island’s environmental history over the last 20,000 years to establish a baseline for conservation efforts. The island is home to some of the most important penguin rookeries in the world, with many other species not found anywhere else. One area the scientists studied was how to protect the penguin-tussock grass relationship, as the native grass provides habitat for penguins and other seabirds and marine mammals and relies on nutrients provided by the animals’ waste. The researchers took sediment core samples from several locations.
By analyzing the pollen and seabird guano, or waste, within the cores, they could determine how penguin and tussock grass populations have fluctuated over time under different climatic conditions. This is part of understanding the wider marine-terrestrial link, which is the connection of nutrients originating in the marine ecosystem that is transferred to the terrestrial ecosystem. In the Falklands region, the soil is very nutrient-poor, making nutrients from the marine ecosystem very important.
Blog



The Pack Ice and Polar Bears of North Spitsbergen

Why a Polar Diving Cruise Should be Your Next Great Decision

10 Popular Bird Watching Binoculars

16 Conversation-Starting Svalbard Facts

Kayaking In Greenland

The Ultimate Traveler’s Guide to the Arctic and Antarctica

Orcas (aka Killer Whales) of Antarctica and the sub-Antarctic

Greenland: Where the Kayak Was Invented

Top 10 Antarctic Attractions

Ancient Arctic Exploration

Arctic Icon: 10 Facts about the Polar Bear

The Emperor Penguin of the Drake Passage

Franz Josef Land Sites, Species, and Experiences

Coming Back from the Brink: The Fur Seals of Antarctica

Svalbard vs. the Canadian Arctic

Life in the Polar Regions

The Seasons of Antarctica: When to Visit and Why

Inside the Svalbard Global Seed Vault

The Research Stations of Antarctica and the sub-Antarctic