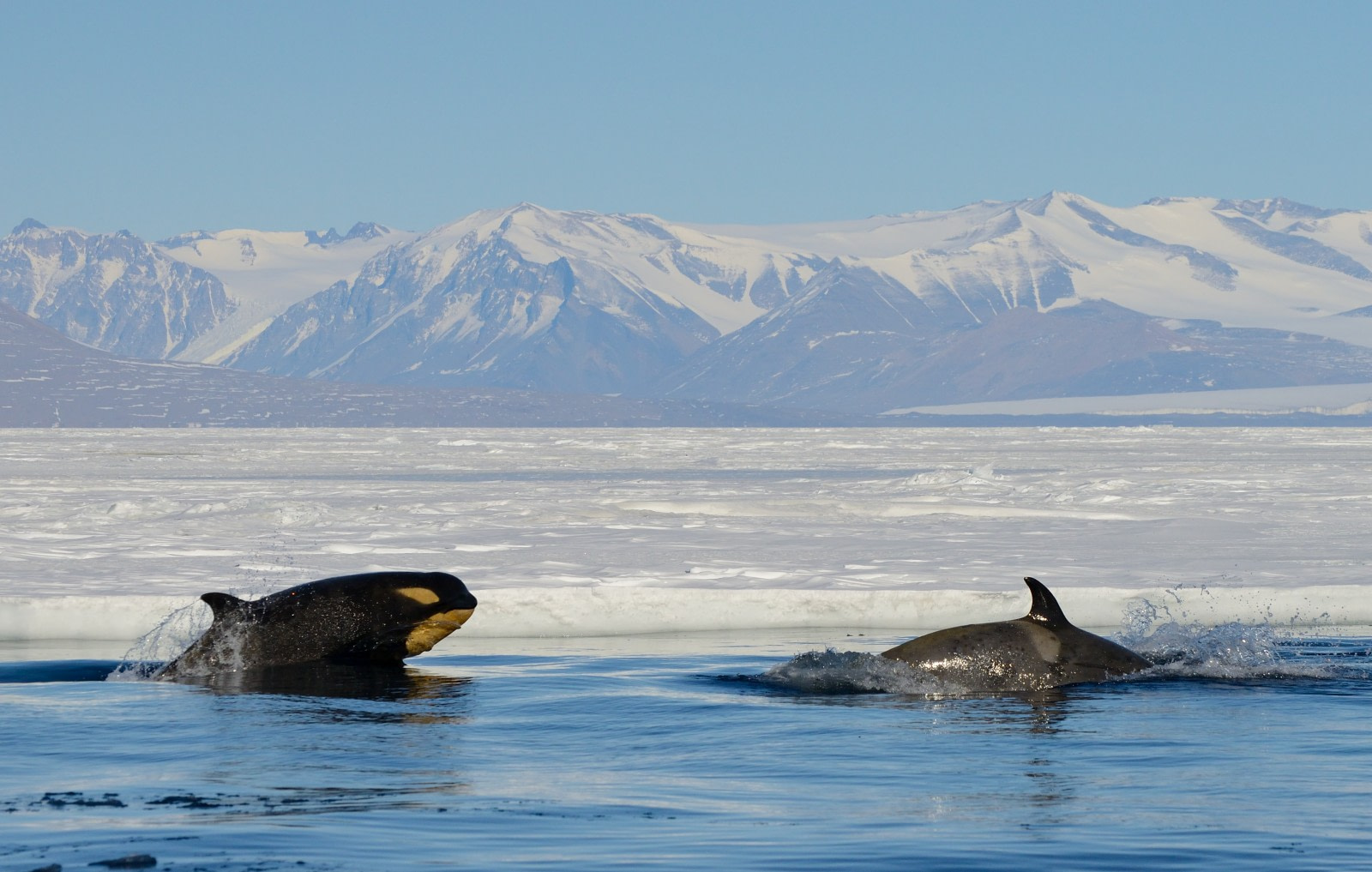
Orcas are highly social and intelligent members of the dolphin family Delphinidae. They are sometimes referred to as killer whales, though this name has somewhat fallen out of fashion due to inaccurately characterizing orcas as ferocious predators.
Found in every ocean, orcas most densely populate the Southern Ocean. Their numbers are estimated between 25,000 - 27,000, making them the third most abundant cetacean in Antarctica. In fact, during the Antarctic expeditions of the early 20th century, British biologists categorized orcas as the most common whale in the Ross Sea. When their ships sailed along the pack ice of Victoria Land, killer whales were observed almost every day.
As we're sometimes lucky enough to see orcas on our own Antarctica trips, here are a few of our favorite killer whale facts in no particular order - ending with a great video in which we cover an additional ten facts about orcas.
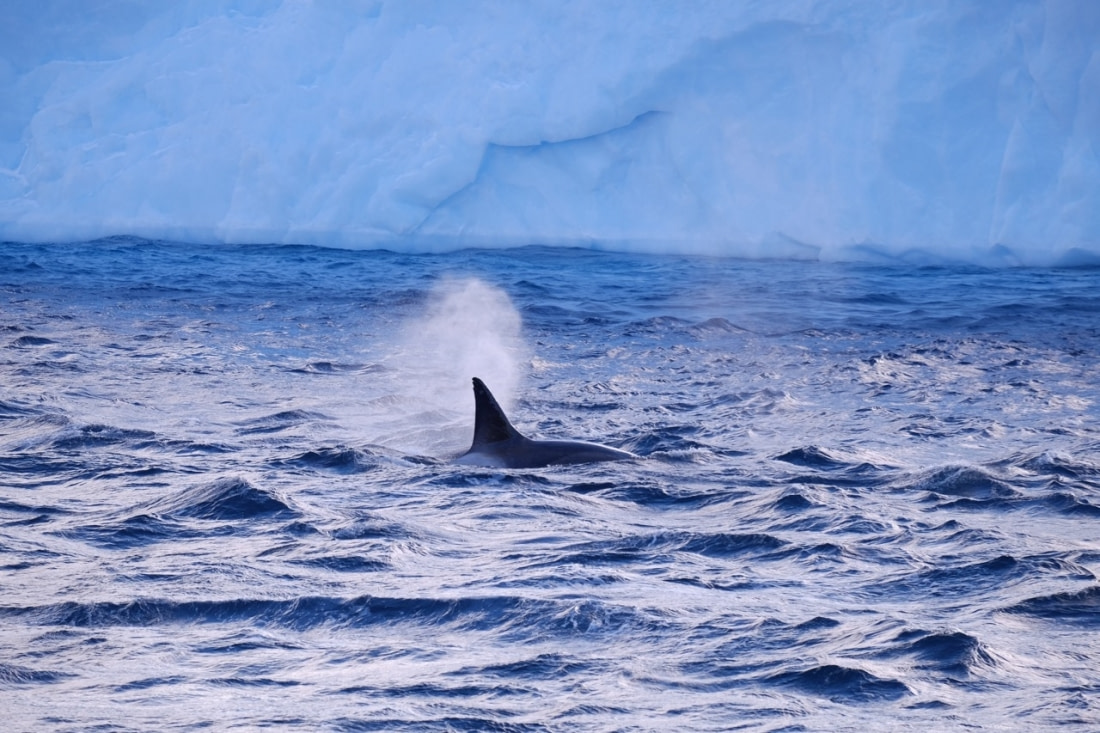

Killer whale size, speed, and dolphin relation
Orcas are among the most recognizable whale species. They have a large black body, white underbelly, and a water patch above and behind their eyes. They also have a gray patch behind their dorsal fins.
Male killer whales can grow up to 10 meters (33 feet) long, with a dorsal fin nearly two meters (6.6 feet) high. Female orcas, on the other hand, are about 20% shorter and have curved dorsal fins less than half the height of killer whale males. Despite their size, orcas are also fast swimmers, and have been observed at speeds of 54 kph (33.6 mph).
And though they are indeed toothed marine mammals, killer whales technically belong to a family of oceanic dolphins. Orcas are the largest members of that family and one of the world's most powerful apex predators, feeding on seals, sea lions, even other whales.
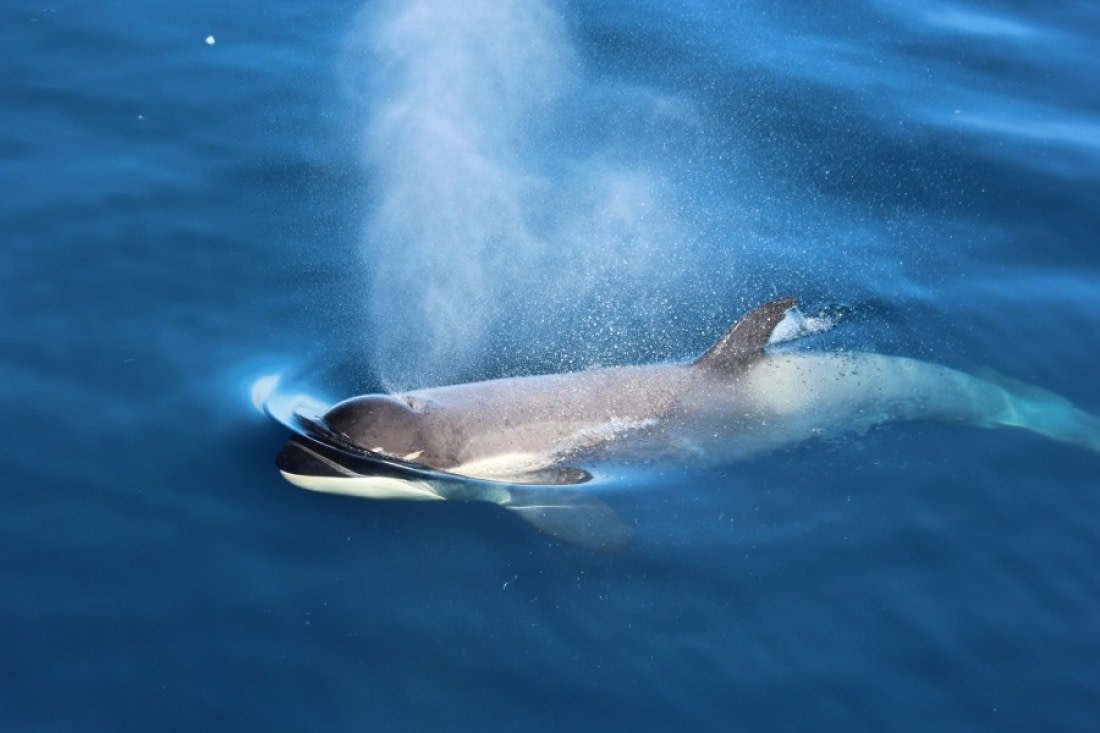

Killer whales hunt in pods comprising up to 40 individual whales. There appear to be both resident and transient orca pods, with resident pods preferring fish while transient pods target marine mammals. All orca pods use cooperative hunting techniques similar to wolf packs, and each pod has its own unique noises that its members can recognize.
Killer whales use echo-location to communicate and hunt, making sounds that travel through the water until they hit an object and bounce back, revealing the object's location, size, and shape.
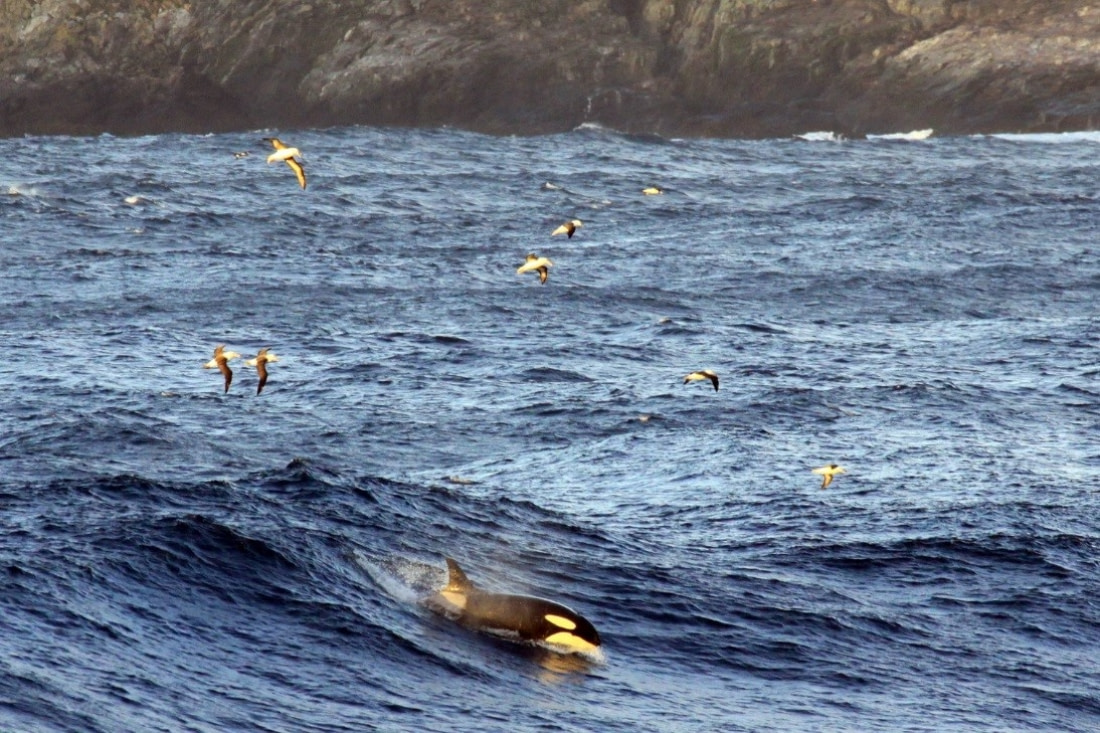

The different types of orca
On your Antarctic or sub-Antarctic cruise, you might encounter these types of orcas:
1. Type A are the largest, reaching up to 9.5 meters (31 feet) long. These orcas prefer to live in open waters of the Southern Ocean, feeding mostly on minke whales.
2. Type B are pack ice whales that are smaller than Type A killer whales, feeding on Weddell seals they manage to knock off the ice floes. Killer whales do this by using their tails and bodies to create waves that wash the seals into the water. There is also a smaller variant of Type B killer whales known as Gerlache orcas, named after the Gerlache Strait off the Antarctic Peninsula. These orcas have an unknown diet but have been seen feeding on penguins, and they are usually spotted around penguin colonies.
3. Type C are known as Ross Sea killer whales, a dwarf species that is the smallest of the three known Antarctic types of killer whale. Males reach around six meters (19.7 feet) in length. Ross Sea killer whales are typically seen around eastern Antarctica in thin pack ice.
4. Type D orcas are the rarest orca and thought by some to be a separate species. They have more rounded heads, no snout, smaller eyepatches, and more narrow and pointy dorsal fins. Type D orcas are seldom seen and in fact were only first recorded in 1955, but their habitat seems to be in the warmer waters just south of South America - indeed, this is where we spotted a type D orca in 2022.
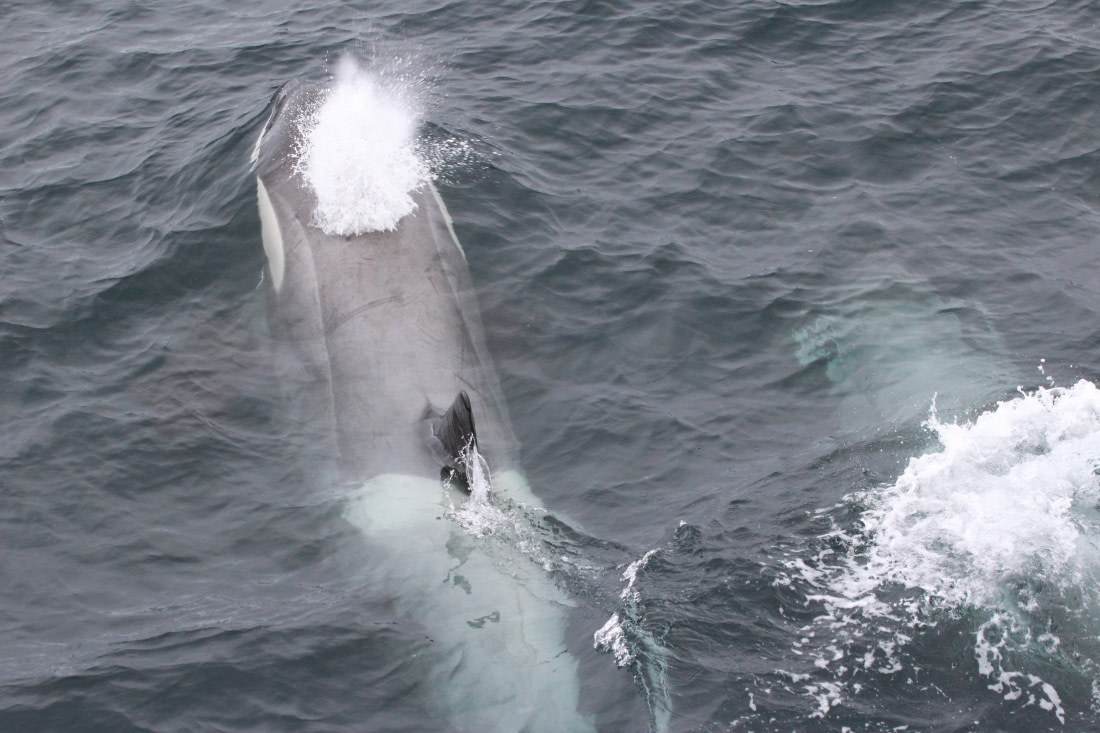

Confirmation of the three Antarctic killer whale types
Killer whales from different eco-types don't breed with one another, which is a criterion for being classified as a different species. However, until recently scientists had not proved these different species of orcas in Antarctica existed, as they had not mapped the entire genome of killer whale mitochondria housing their DNA.
But in 2013, after sampling 139 killer whales from the North Pacific, North Atlantic, and the oceans surrounding Antarctica, scientists were able to see clear differences between each species of killer whale. The researchers believe that Type B and C killer whales are genetically similar, because their lineage diverged from other orcas around 150,000 years ago – just a moment in evolutionary terms.
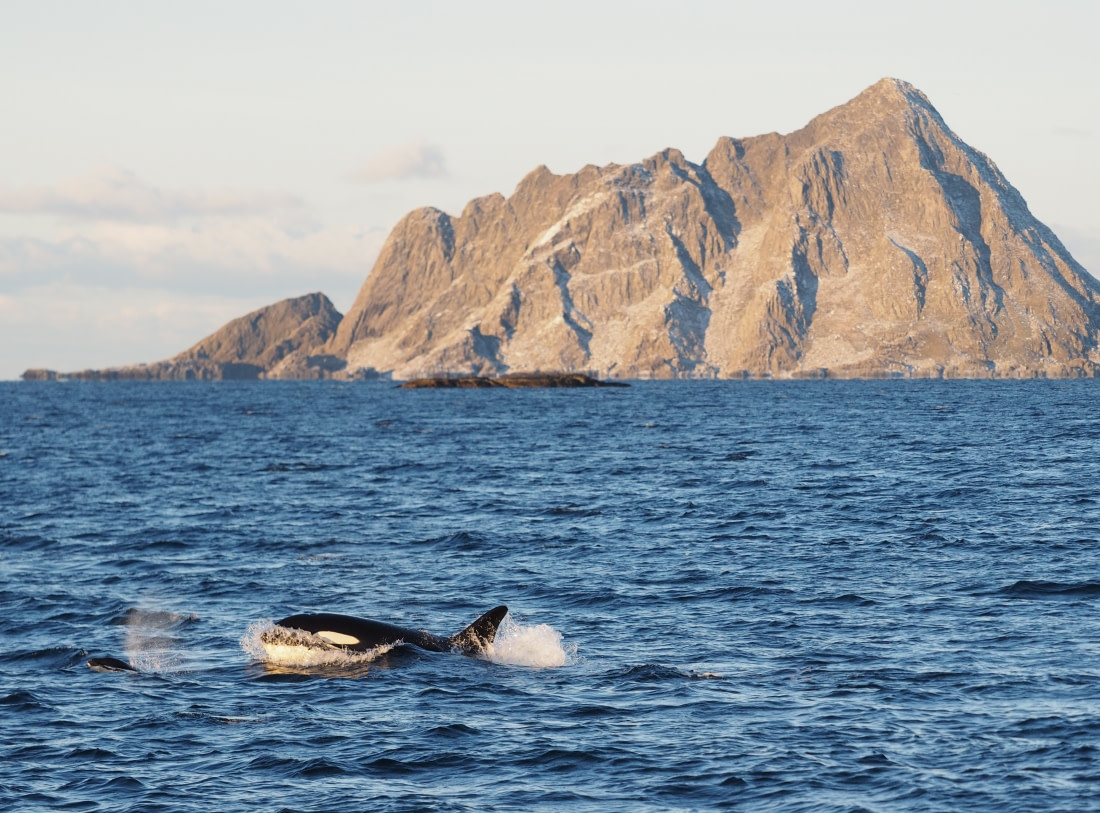

Ross Sea killer whales (type C orcas) and their diet
Type C orcas are observed to have a specialized diet focusing on Antarctic toothfish, though the exact reason for this is unknown. Killer whales in the Ross Sea, near McMurdo Sound, have been commonly spotted carrying toothfish in their mouths.
A comparison of the nutrient density of toothfish with other prey shows that toothfish represent a higher-energy food source than other Ross Sea fish.
Scientists don't know the extent to which toothfish forage or how deep Type C killer whales can dive, but in some studies orcas are estimated as diving to 200 - 400 meters (650 - 1,300 feet) with a maximum of around 700 meters (2,300 feet).
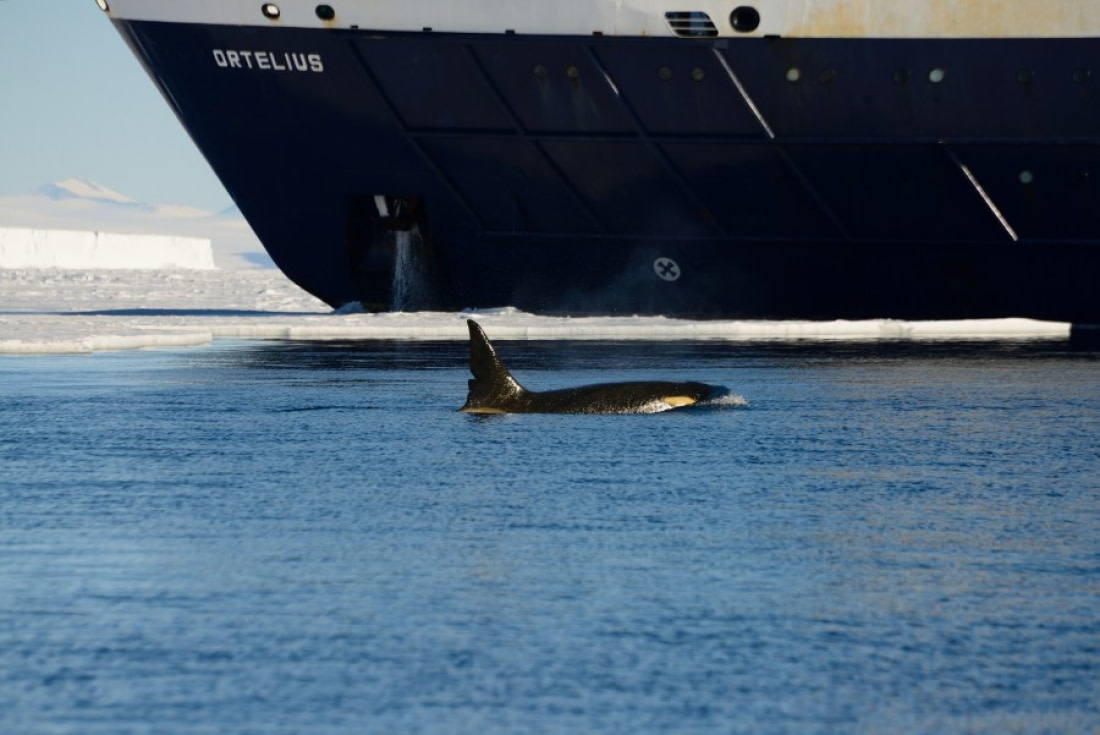

To understand more about Ross Sea orcas, the GEMM Lab of Oregon State University has collaborated with New Zealand scientists from the National Institute of Weather and Atmosphere (NIWA) and Gateway Antarctica of the University of Canterbury, collecting ecological data on Type C killer whales in the Ross Sea.
During a pilot project in McMurdo Sound in January 2014, these researchers recorded and photographed three observations of orcas with Antarctic toothfish prey. Because these observations occurred during the late summer break-up of fast ice over shallow coastal waters, the scientists hypothesized that toothfish are the main prey for Type C killer whales, at least during the summer.
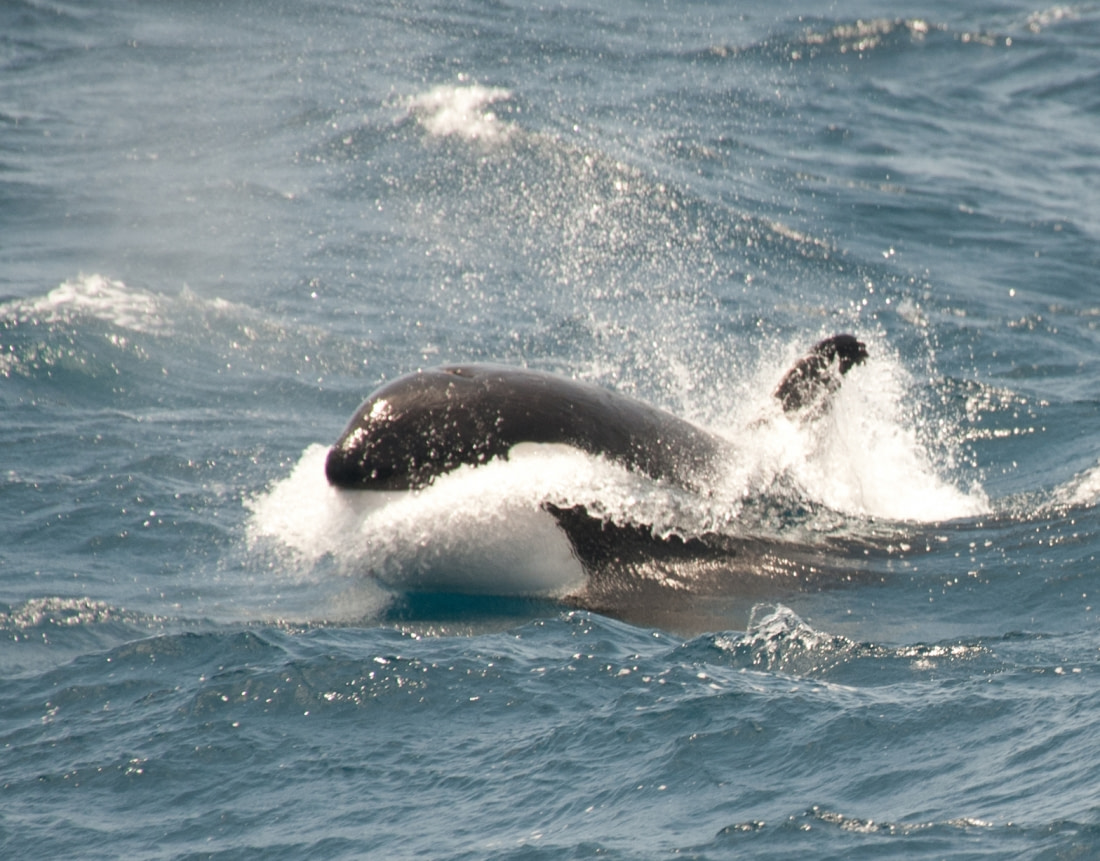

Ross Sea orcas commuting between Antarctica and New Zealand
New Zealand and Italian scientists have discovered that Type C killer whales swim 4,900 km (3,050 miles) from Antarctic to northern New Zealand.
Gateway Antarctica's Regina Eisert led a team to Scott Base during the 2014 - 2015 Antarctic summer that studied killer whales as part of a research program on the Ross Sea ecosystem that involved NIWA, Landcare Research, and Lincoln University. The aim of the study was to determine the importance of toothfish and where killer whales feed in the Ross Sea.
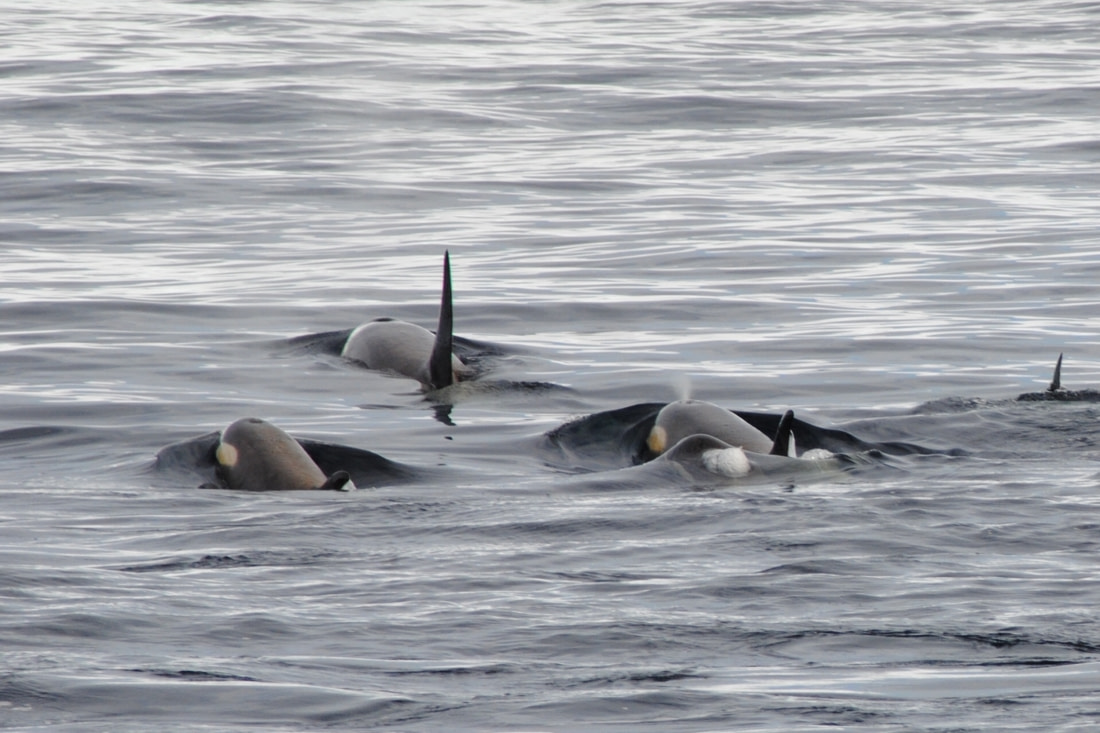

At the same time, 360 km (224 miles) north of Scott Base, Italian whale experts Giancario and Simone Panigada used satellite transmitters on killer whales in Terra Nova Bay to determine orca movements. Eisert said the two teams hit research gold when they independently verified that Type C killer whales were making long journeys between Scott Base and the warmer waters off Northland, New Zealand.
One researcher, Ekaterina Ovsyanikova, found the same female Type C killer whale had been photographed numerous times in New Zealand and McMurdo Sound. The research team found that the average orca commute took 22 days.
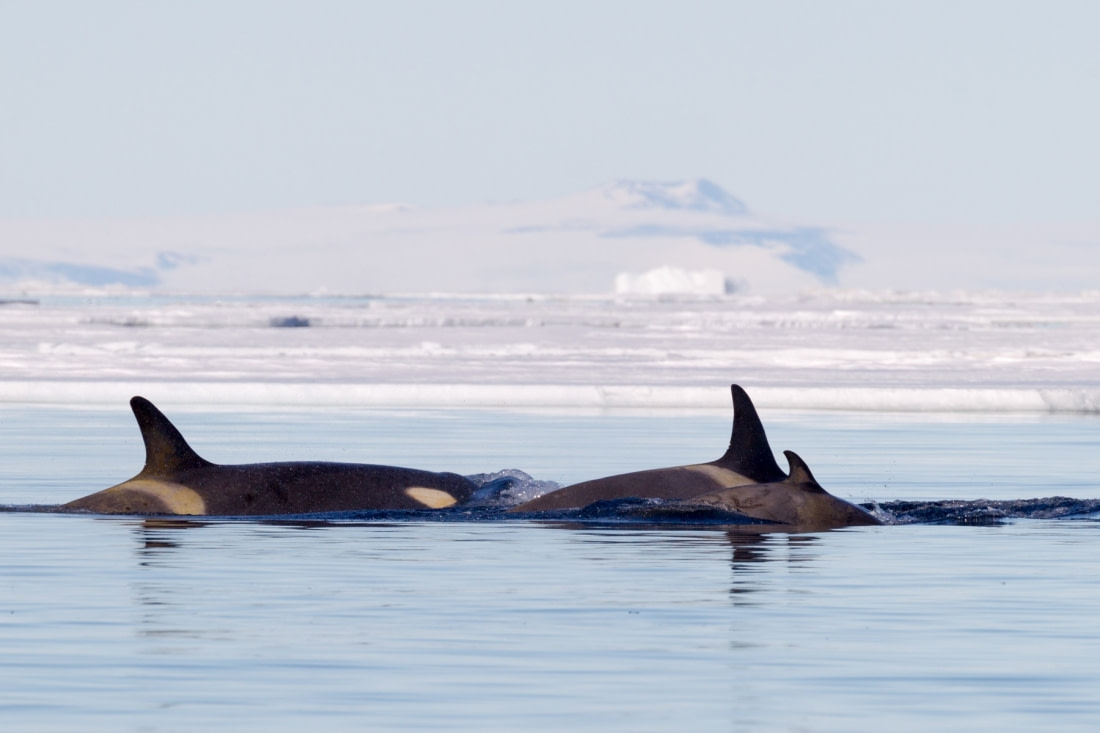

Digital database to track Ross Sea killer whales
The scientists from New Zealand have collaborated with Ingrid Visser from the Orca Research Trust as well as other researchers to create the first open-access photo-ID catalogue for Antarctic killer whales from the Ross Sea.
Photo identification is the main non-invasive research tool used to study orcas. Slight differences in color, nicks on the fins, and scars on the killer whale's body uniquely identify each orca, allowing individual killer whales to be recognized wherever they go.
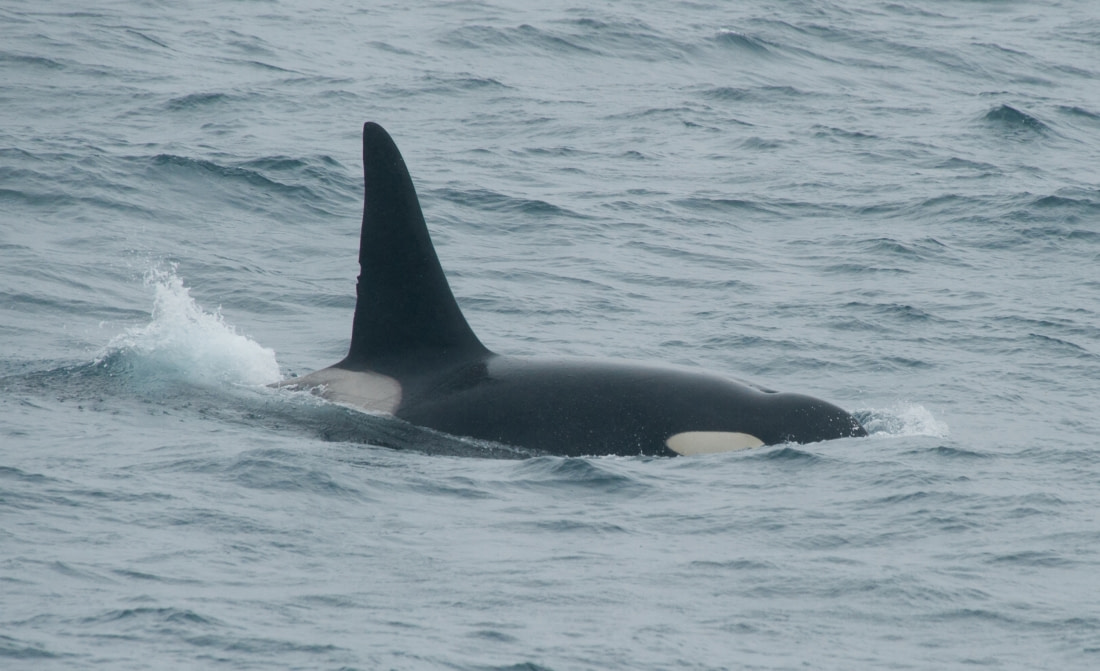

Compilation of killer whale images into catalogues enables researchers to follow individual orcas in time and space, making estimations of their total population size. Visser is also investigating the possibility of hosting a killer whale photo ID on Antarctica New Zealand's digital asset management platform, launched in June, 2015.
This database, created by Wellington technology company NZMS, is based on a non-hierarchical network structure similar to the human brain, providing a matrix to curate, access, and grow the killer whale photo-ID catalogue.
All these advancements will help ensure these intelligent whales are better understood and, hopefully, far better respected.
Ten orca facts video
If the fount of killer whale facts above has left you wanting more, below is a great video with ten of our favorite facts about orcas. We hope you enjoy it before joining us to see these magnificent marine animals in person!
Blog



Gough Island: Seabird Capital of the South Atlantic

The Dirty Details of Antarctica's Dry Valleys

The Northern Lights dancing across the skies

Hondius Photography and Video Workshops

The South Georgia Seven: Hikes, Fjords, Whales, & Penguins

The Enchanting Islands of Svalbard

Solargraphy & Pin Hole photography in the Arctic

Earth vs. Mars: Polar Regions Compared

Book Recommendations for Your Polar Cruise

Explore Antarctica Without Leaving Your Couch

10 Common Misconceptions About the Arctic

5 Life Lessons You'll Learn in Antarctica

Tracking Greenland’s Wildlife from Space

Encounter with the emperor penguin in Antarctica

Why a Polar Diving Cruise Should be Your Next Great Decision

Orcas of the Polar Seas

Baleen Whales – The Gentle Giants of the Ocean

Polar Amore: 14 Wildlife Pics to Warm up Your Valentine’s Day

Greenland: East vs. West