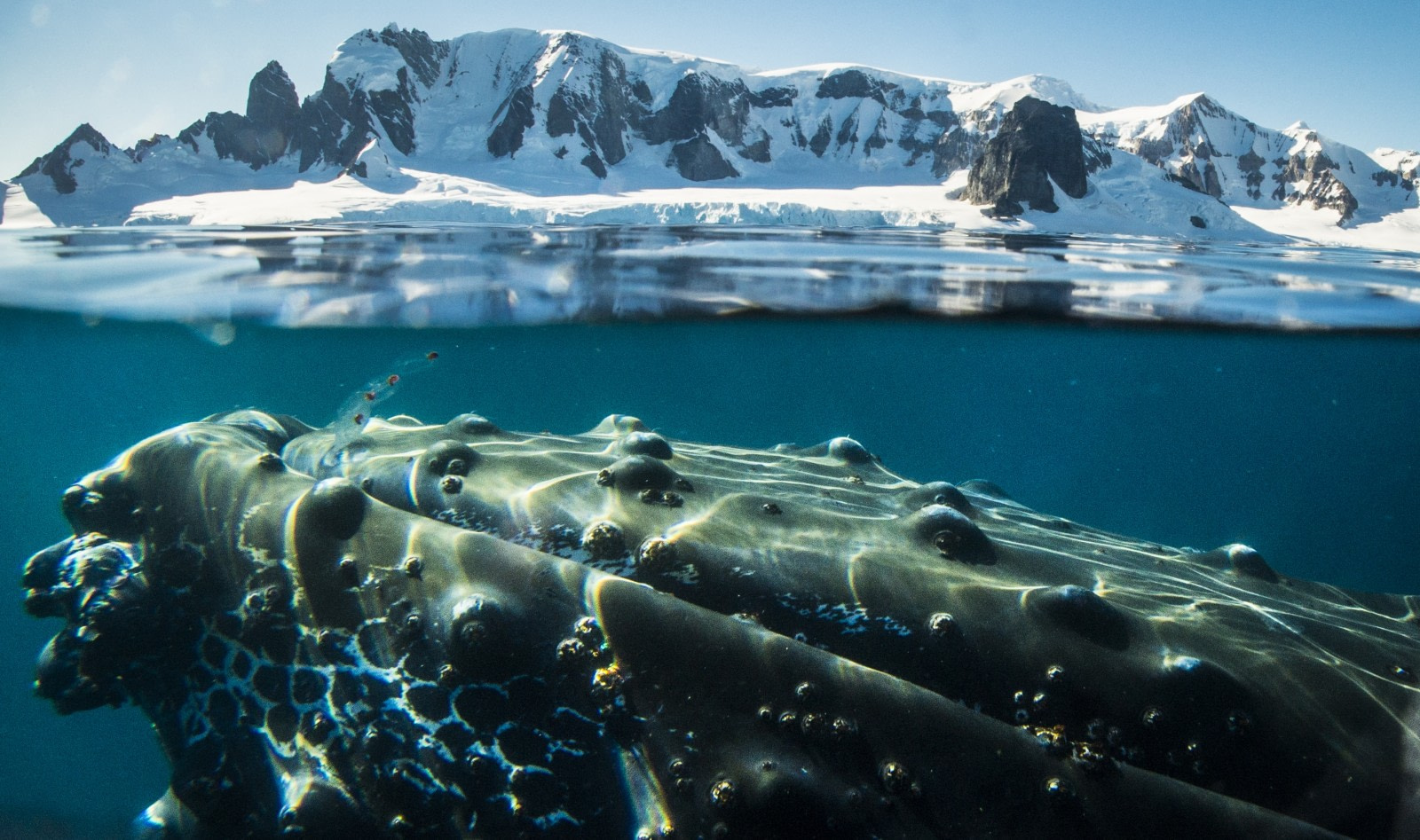
They are the largest animals on Earth, yet they thrive on some of the tiniest creatures. These giants can reach lengths of 30 meters (90 feet), but it is the microscopic zooplankton, krill, and small fish that sustain them. These are the baleen whales. Unlike toothed whales, baleen whales lack teeth. Instead, they use plates of baleen in their mouths to trap and consume their tiny prey.
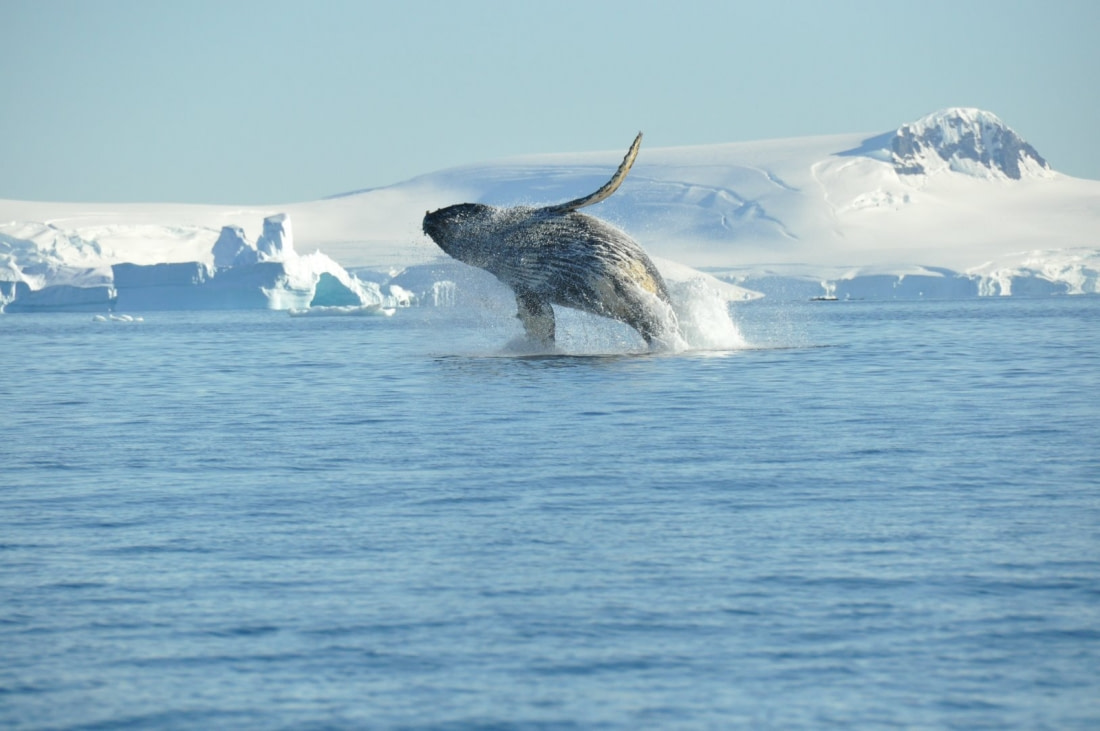

The baleen are comb-like filaments, part of the whale’s mouth structure. Baleen is a protein similar to the keratin found in human fingernails and hair. When feeding, these whales take in large quantities of ocean water, straining it to capture their food. Another unique feature of baleen whales is their paired blowholes, unlike toothed whales that have a single blowhole.
Some baleen whales feed by swimming with their mouths wide open to capture water and prey near the surface, known as lunge feeding. Others stay below the surface, opening their mouths to ingest large amounts of water. When they close their mouths, the water is expelled through the rows of baleen, trapping the food.
Types of baleen whales you can spot
There are many species of baleen whales, ranging from the approximately 2-meter (6 feet) pygmy Right whale to the enormous blue whale. In total, there are 15 known species. Some of the baleen whales spotted on Arctic cruises include the minke, fin, sei, blue, humpback, and bowhead. Among the toothed whales, orcas, sperm whales, Northern bottlenose, narwhal, and beluga have been sighted.
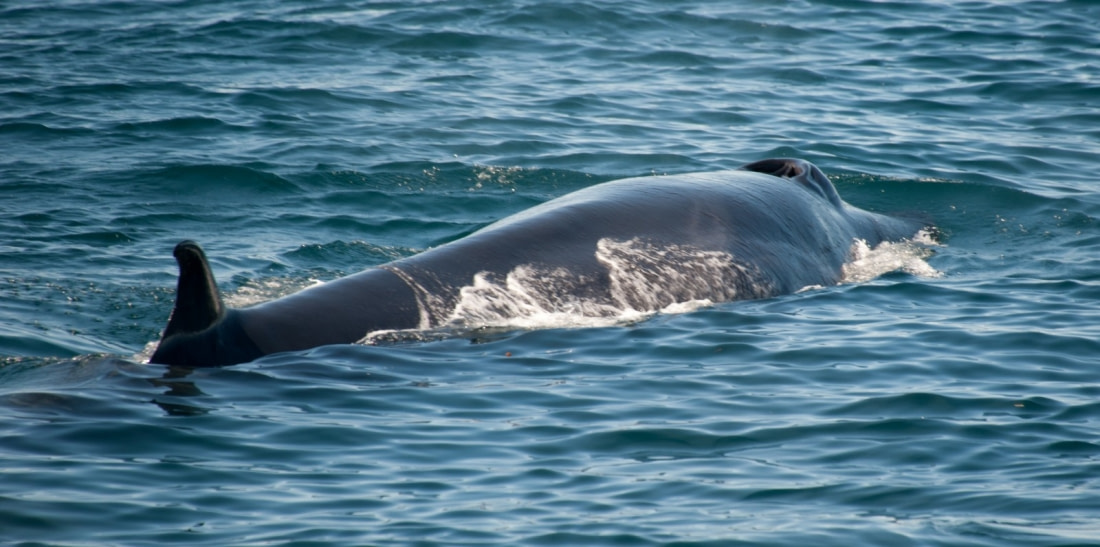

How baleen whales swim
Like penguins, sea turtles, and otters, baleen whales have flippers that help propel them forward and steer. Unlike those other species, whales have a large rear fluke, which they raise and lower to create forward motion. Some whale species are known to leap out of the water to gain additional speed when necessary.
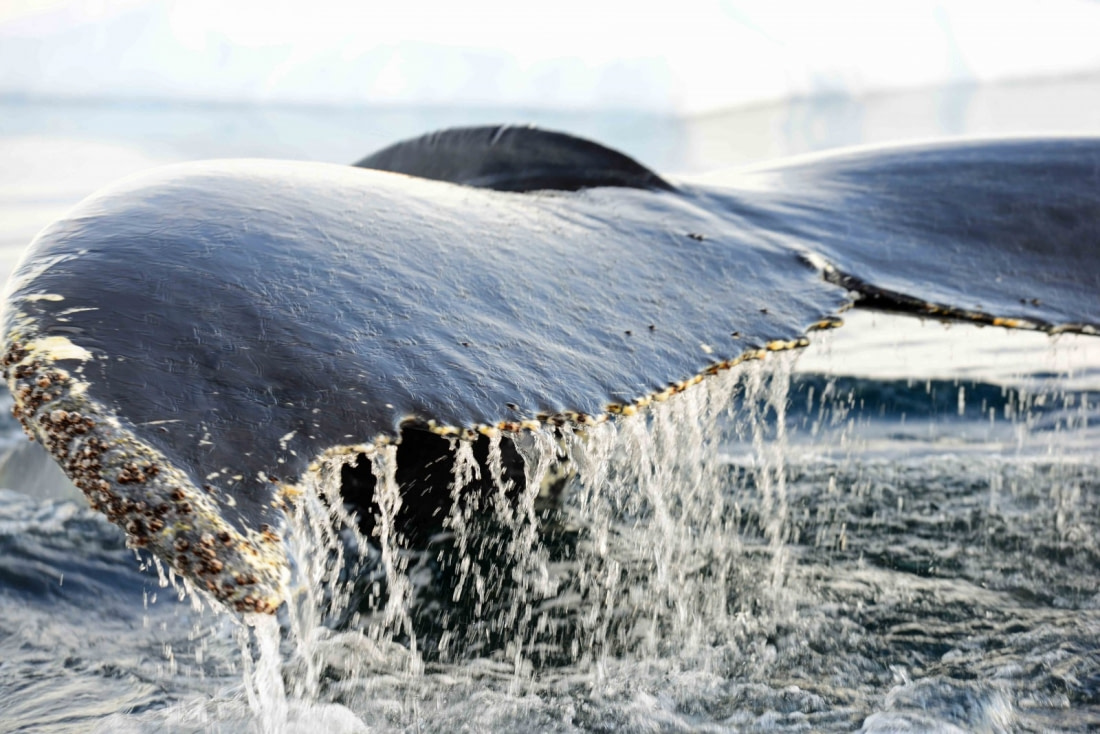

The baleen are expert divers
Baleen whales are expert divers, with some reaching depths of 470 meters (1,540 feet). Their unique anatomy has evolved to make such dives possible. Their lungs are designed to collapse under the immense pressure of deep dives, preventing damage. Baleen whales’ lungs are also highly efficient at extracting oxygen from the air, about four times more efficient than human lungs. Their heart rate drops to around 10 beats per minute to conserve oxygen during dives.
However, as mammals, whales must periodically return to the surface to breathe. They breathe through blowholes located at the top of their heads. When surfacing, they expel carbon dioxide dramatically, spraying surrounding seawater into the air, leading to the classic whaling expression, “Thar she blows!”
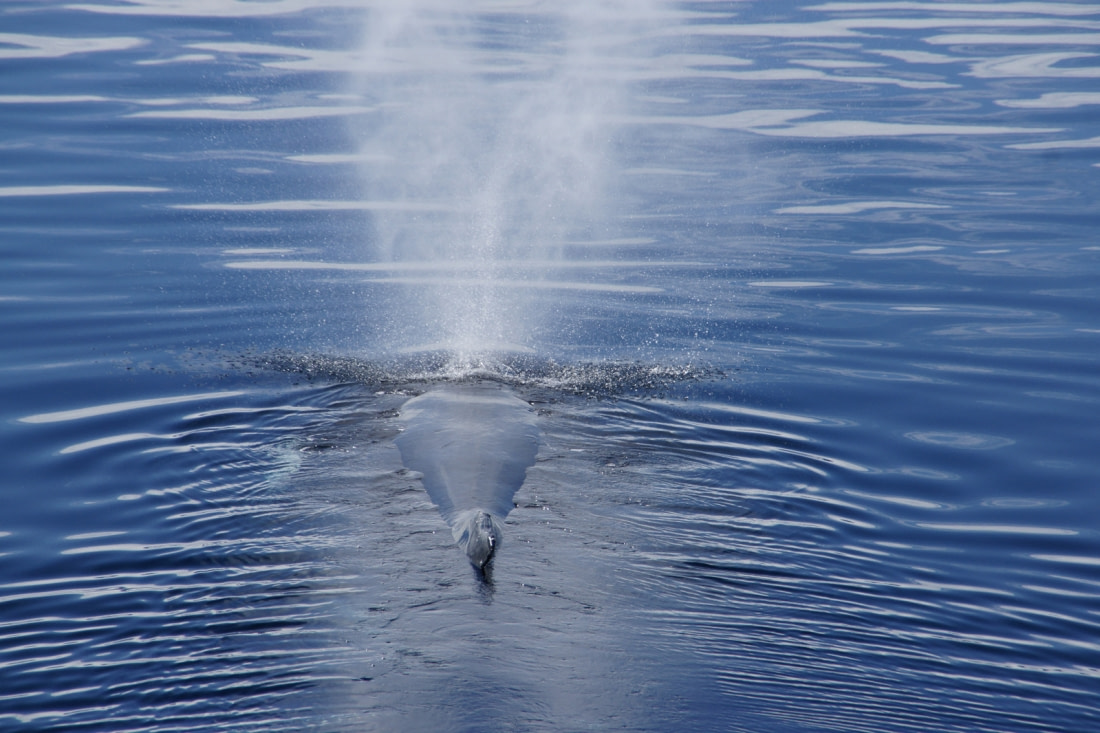

Reproduction & whale song of the baleen whale
During the breeding season, baleen whales communicate or “sing.” It is believed they use folds in their larynx to produce sounds. The blue whale’s low-pitched song can be as loud as 190 decibels and heard hundreds of kilometers away. The humpback whale sings the most complex songs, consisting of groans, roars, and chirps, often repeated for hours. It is thought that all male humpbacks from a specific geographical area sing the same songs throughout the breeding season.

The whale gestation period is about a year, during which they grow rapidly. Shortly before birth, a blue whale fetus gains around 100 kg (220 lb) per day and measures about 7 meters (23 feet) long at birth. During nursing, the calf can gain 80 kg (180 lb) a day. By the time they reach sexual maturity at 5-10 years, they will have grown to a length of 20-24 meters (66-79 feet). Whales can live up to 80-130 years, with 19th-century harpoons found in deceased whales indicating this remarkable longevity.
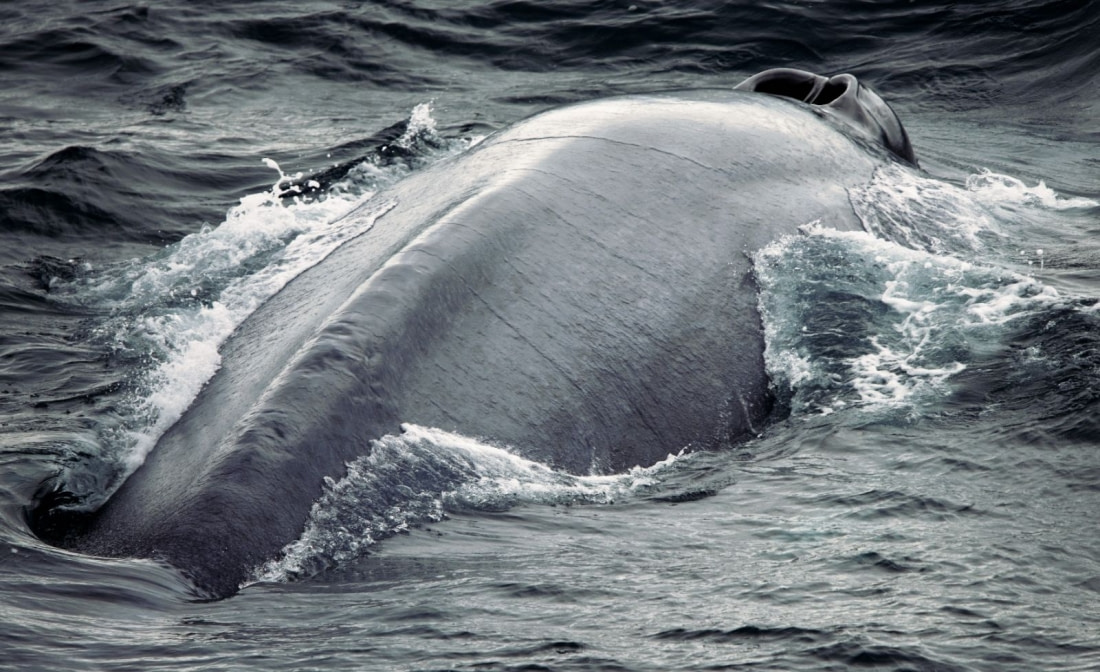

Why do baleen whales migrate?
Baleen whales migrate for several reasons, primarily related to calving and newborns. Young baleen whales have not yet developed a thick layer of blubber to insulate them from cold Arctic waters, prompting migration to warmer tropical climates. Warmer waters are also thought to be safer for calves, protecting them from predators like killer whales.
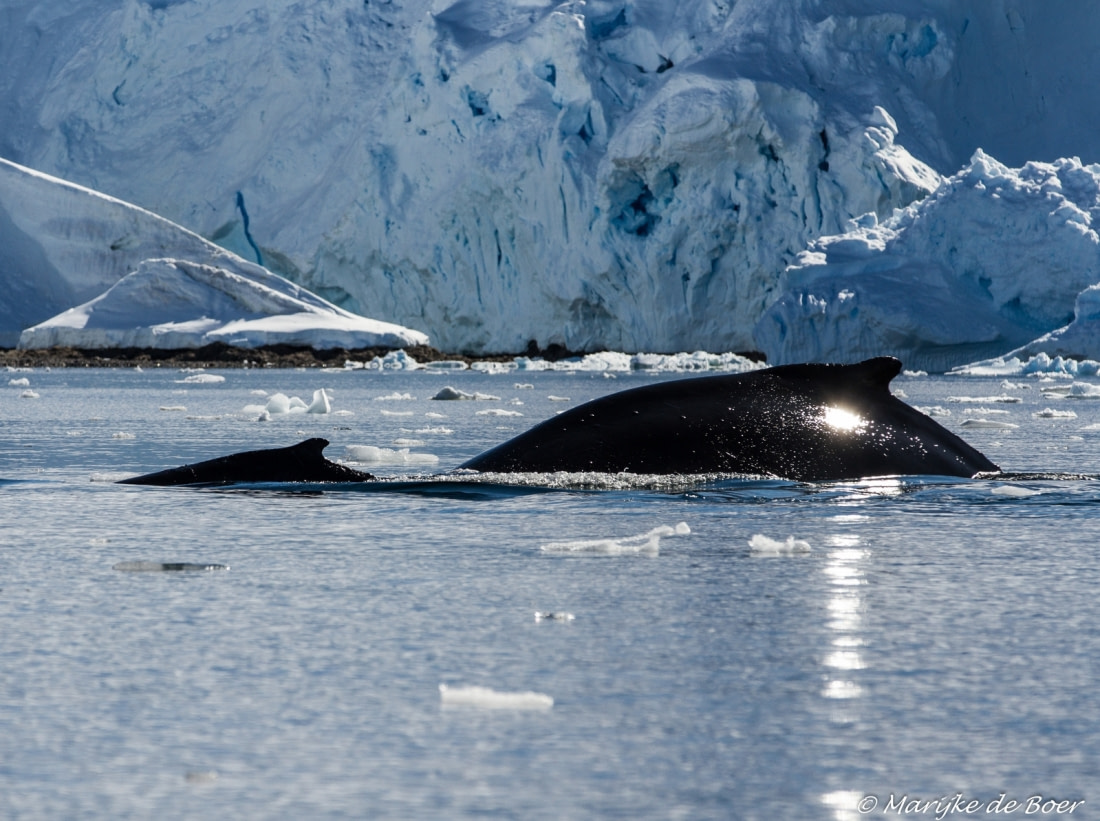

In spring and summer, baleen whales migrate back to Arctic waters to feed on abundant plankton blooms. Some, like the gray whale, migrate as much as 23,000 km (14,000 miles) from the Arctic to the Baja Peninsula and back.
Whale hunting: an ancient story
For thousands of years, humans have hunted whales for food and oil. The Inuit hunted whales throughout the Arctic Ocean for their blubber and baleen. In the 19th century, whales were also hunted for their whalebone, used in women’s corsets, buggy whips, and umbrellas.
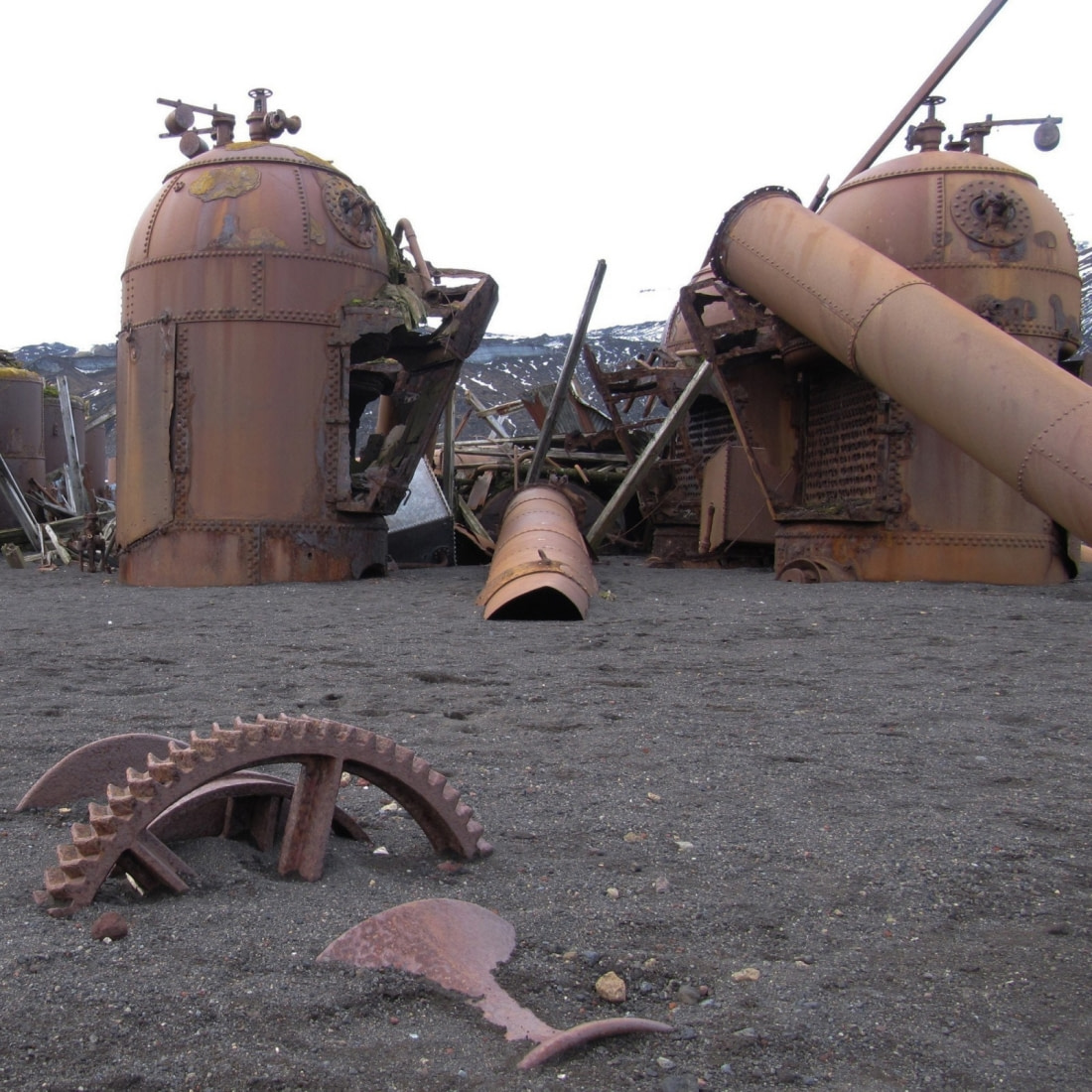

With no controls on hunting activity, whale populations eventually became depleted. It wasn’t until 1982 that the International Whaling Commission placed hunting limits to protect whales from extinction. Most countries have now ceased all whaling activities. However, humans are not the only predators of baleen whales. Calves and newborns are also preyed upon by killer whales.
Other threats to baleen whales include climate change, which has led to declines in sea ice, affecting their habitat, and ocean acidification. Additionally, commercial shipping poses a hazard. Baleen whales cannot always hear the low-frequency propeller noise and may be unaware of a ship’s presence until it is too late. Sonar used by ships also interferes with whale vocalizations, complicating their communication.
Conservation and the future of the baleen whale
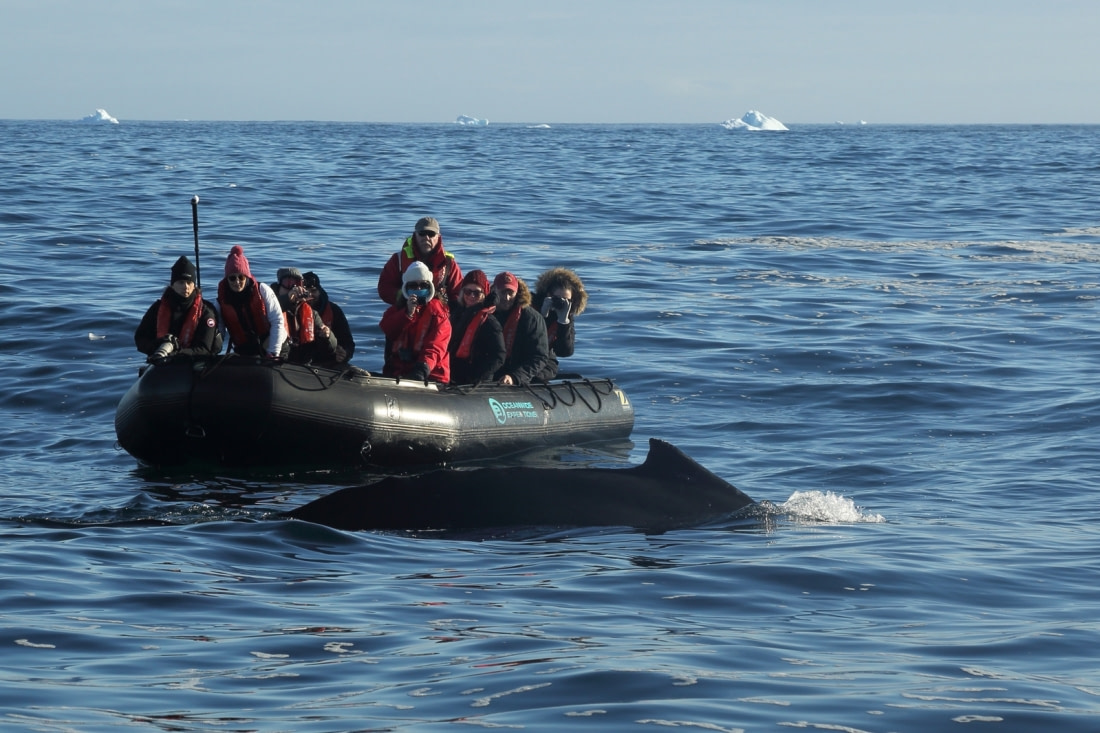
Over the last 30-40 years, efforts to slow down and halt whale hunting have increased. This has been accompanied by movements to promote whale watching, which serves both recreational and scientific purposes. A 2009 study estimated that 13 million people go whale watching annually, generating over $2 billion in tourism revenue worldwide. Many countries have now ceased all whale hunting activities, while others observe strict limits.
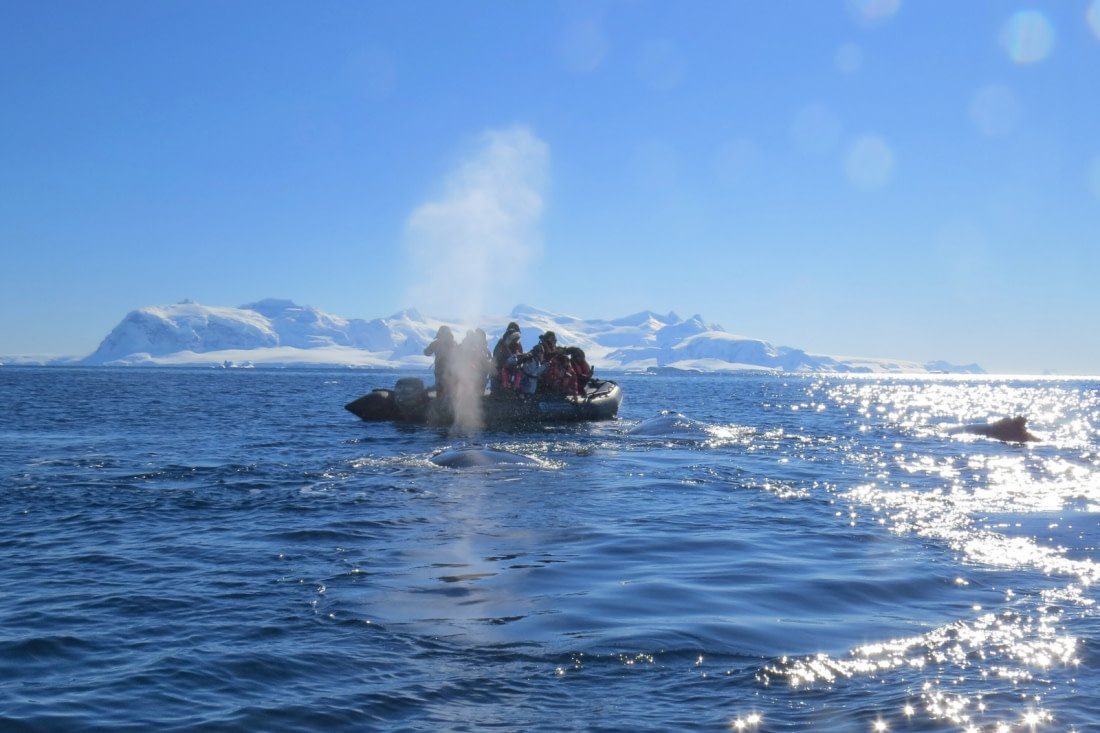

There are many humane reasons for this, but perhaps the most practical one is voiced by conservationists: a whale is worth much more alive and watched than hunted and dead.
Blog



Five Birds You Might See on Your Greenland Cruise

Camping in Antarctica: a True Expedition Experience

12 Things to Do in Antarctica

Port Pastimes: 7 Fun Things to Do in Longyearbyen

Five Reasons to Love St. Helena

North Norway, Northern Lights, and All the Pretty Whales

The Arctic Hare: Easter Bunny

Birds of the South: 33 Antarctic Birds and Seabirds

10 Tried-and-True Bird Photography Tips

Top 10 Antarctic Attractions

The Research Stations of Antarctica and the sub-Antarctic

Polar Cruises: The Ultimate Icebreaker
The History of Antarctica in Maps

The Giant Petrels of King George Island

The bowhead whale, whaling about the Arctic

Not Eskimos: 10 Enlightening Facts About the Inuit

How Arctic Wildlife Differs from Antarctic

Book Recommendations for Your Polar Cruise

A Bug’s Life in Svalbard