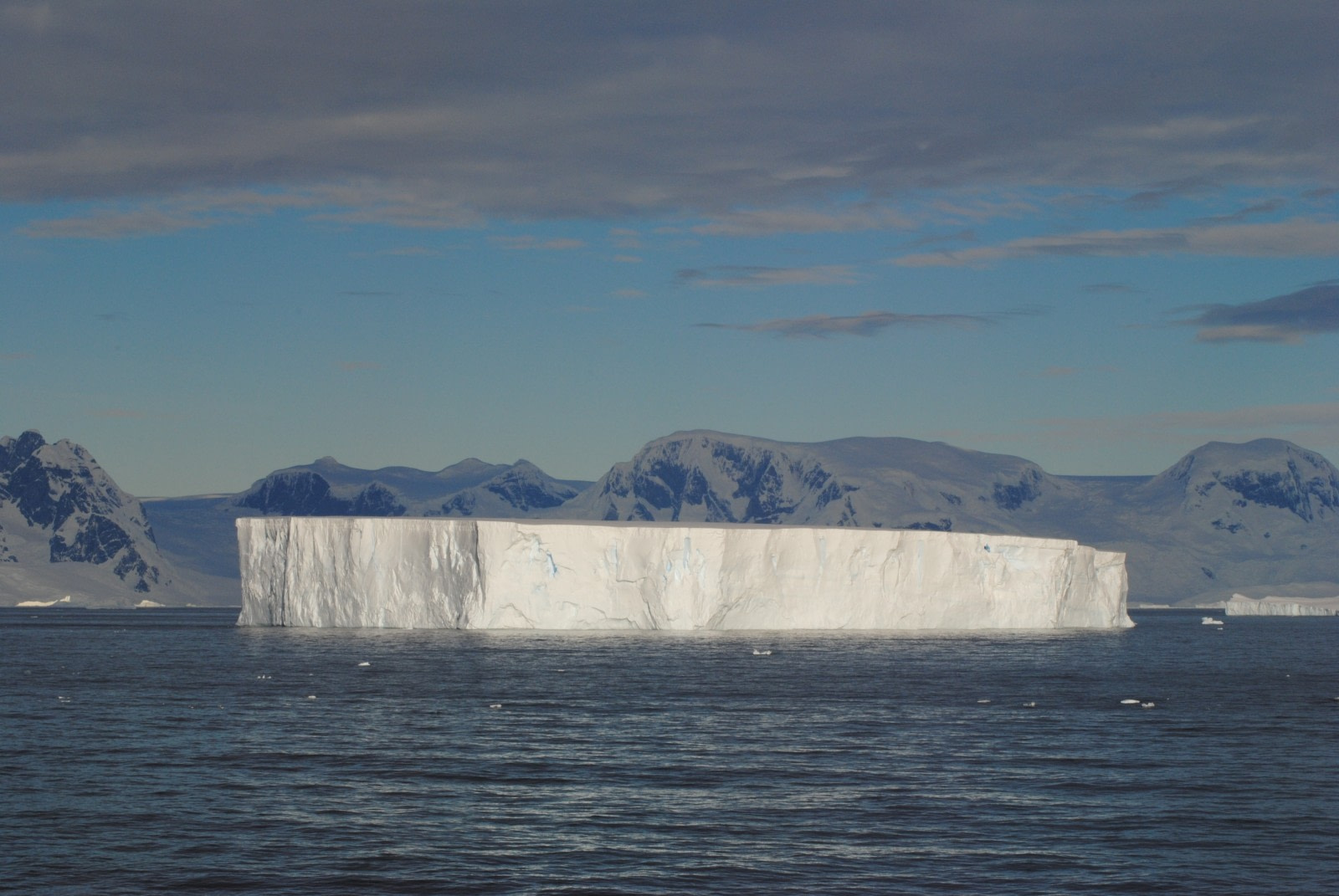
The continent you'll explore during your Antarctica cruise is far more than just an ice-covered land with penguins, whales, and seals. Beneath the thick ice lie hidden freshwater lakes teeming with thousands of microbes, hinting at a diverse array of life. In 2013, a team of researchers obtained the first uncontaminated water sample ever retrieved directly from an Antarctic lake.
Lake Whillans, located 800 meters below the ice and 640 kilometers from the South Pole, spans nearly 60 square kilometers but is only 2 meters deep. Given its pristine condition, the team spent six years developing a method to extract the sample without contaminating the water with drilling equipment or invasive organisms. They used ultraviolet radiation, water filtration, and hydrogen peroxide to sterilize both the machinery and the water used to bore through the ice.
Life under the ice
After a year of sampling, the results revealed an abundance of life, with the team finding 130,000 cells in each milliliter of lake water, including nearly 40,000 bacteria and archaea. The sample also indicated that life has survived in the lake without solar energy for the past 120,000 years, possibly even up to 1 million years.
Over the past year, researchers have isolated and grown cultures of about a dozen species of microbes. DNA sequencing has revealed signs of nearly 4,000 species, many of which are known microbes that break down minerals for energy in the absence of sunlight.
One main question for scientists is whether these forms of life are classified as 'survivors' or 'arrivers.' Survivors are descendants of microbes that lived in the sediments when the area was covered by the ocean, while arrivers would have been deposited on the ice and worked their way down over the past 50,000 years as ice melted off the bottom of glaciers.
Alternatively, arrivers could have entered the lake from seawater seeping under the ice sheet, given that Lake Whillans is 100 kilometers from the grounding line where the ice sheet transitions from resting on the ground to floating on the ice. Other important findings from the lake included traces of fluoride, suggesting the presence of hydrothermal vents, which provide rich sources of chemical energy that can support exotic life. Small amounts of formate, a chemical indicating the presence of methane, a greenhouse gas, were also found.
Estimates suggest that sediments under the Antarctic ice sheet contain hundreds of billions of tonnes of methane. This poses a significant issue as global temperatures rise and Antarctic ice sheets begin to melt, releasing methane and contributing to global sea level rise.
The West Antarctic glacier system melting
In 2014, scientists released studies revealing that a large section of the glacier system in West Antarctica has started to collapse. Previously, scientists believed the 3.2-kilometer-thick glacier system would remain stable for thousands of years, but new research suggests a faster timeline.
UC-Irvine Earth science professor and lead author of the study, Eric Rignot, warns that six large glaciers in the Amundsen Sea "have passed the point of no return," with current estimates suggesting the glaciers could disappear within two centuries. If this happens, the rest of the ice in West Antarctica would follow.
Meanwhile, a study on the thinning of glaciers on the Southern Antarctic Peninsula has found that a major portion of the region has destabilized since 2009, with ice-mass loss of the marine-terminating glaciers rapidly accelerating.
Warm water contributing to melting
One explanation for the rapid melting of glaciers is that warmer seawater is penetrating the glacier base. Researchers studying the Totten glacier in East Antarctica have found evidence of a trough deep beneath the glacier, allowing warmer seawater to penetrate its base. During a recent voyage to Antarctica, researchers found waters around the Totten glacier to be 1.5 degrees Celsius warmer than other areas.
This discovery surprised scientists, as the East Antarctica ice sheet was previously thought to be surrounded by cold waters and therefore very stable. Due to warmer waters, "the Totten glacier is the most rapidly thinning glacier in East Antarctica, and this melt has the potential to drive substantial regional ice loss," according to Jason Roberts, an Australian Antarctic Division glaciologist.
Warmer and more productive ocean
New research has found that while rising global temperatures will intensify glacial melting, coastal Antarctic waters could become more productive. This is due to polynyas—expanses of open seawater along the coast enclosed by floating sea ice and the continental shelf—forming. These formations are productive with an abundance of phytoplankton due to iron being pumped into them by glacier meltwater. This results in polynyas emitting a smell similar to rotten eggs, according to Kevin Arrigo, a biological oceanographer at Stanford University, due to the emissions produced by phytoplankton.
Using satellite data from 1997 to 2014 for 46 polynyas around Antarctica, researchers detected a strong correlation between productivity levels and the extent of glacial melt from adjacent glaciers. The scientists hypothesize that glacier meltwater enriches the waters of the polynyas with iron, which acts like a fertilizer. The meltwater supplies iron because, as melting ice moves towards the ocean, it breaks down bedrock, which is rich in iron. Glaciers also have iron trapped in their mass from the snow that has accumulated on ice sheets over thousands of years, with falling snow trapping dust rich in iron.
Productive oceans acting as carbon sinks
The researchers speculate that as the ecosystem becomes more productive, more food will be available for organisms at the top of the food chain. Arrigo notes, "the largest density of penguins and seals are in the areas where polynyas are most productive." Another potential benefit is their role as carbon sinks, as bodies of water with photosynthesis occurring act as carbon sinks. In particular, Arrigo claims that polynyas "disproportionately suck atmospheric carbon dioxide," and an increase in their productivity is likely to enhance their ability to store carbon. Nonetheless, with polynyas being only a few hundred square kilometers in size, Arrigo admits their impact will be minimal.
Blog



Weddell seals: The data collectors scientists of Antarctica

8 Scientific Wonders of the Arctic

Graham Land: A landscape dominated by volcanoes

A Day on m/v Plancius

Ancient Arctic Exploration

Antarctica’s Hourglass Dolphin

The Impact of Small vs. Large Cruise Ships

Hondius Photography and Video Workshops

What to Expect When Crossing the Drake Passage

Bouvet Island: The Most Remote Island in the World

Antarctic krill: Antarctica's Superfood

Explore Antarctica Without Leaving Your Couch

Freshwater ecosystems in the Arctic

Large and in Charge: Antarctica’s Southern Elephant Seals

The Pack Ice and Polar Bears of North Spitsbergen

Visiting the Nearly Unknown: New Zealand’s Campbell Island

The Emperor Penguin of the Drake Passage

Book Recommendations for Your Polar Cruise

16 Conversation-Starting Svalbard Facts