Last Valentine's Day we gave you 14 wildlife pictures highlighting the ins, outs, ups, and downs of polar romance. This year we're moving on to something a little more advanced: the nitty-gritty details of polar wildlife breeding rituals.
In other words, it's time to turn on the Marvin Gaye.
Here we'll explore the breeding practices of five polar animals in all their Arctic, Antarctic, and sub-Antarctic steaminess. Included are some of the most iconic species, from polar bears to emperor penguins, walruses to wandering albatrosses. By the time we get to humpback whales, you'll need the world's coldest shower - or polar plunge, if you swing that way.
So drop the curtains, get the kids out of the room, and do your best not to fog up the screen.

1. Knocking boots like a polar bear
From a very early age, polar bears are open for business.
Male bears start following the scented tracks of fertile females around age six, and females begin laying down said stank around age four to five.
Polar bear bachelors can be a bit thuggish when competing for females, getting into scraps that might leave both combatants with scars, chipped teeth, and some seriously hurt feelings. But by the time pairs have formed for the season, things tend to get more peaceful.
Mating lasts about a week, after which female polar bears take off to gorge themselves on raw seal and Doritos. They often double their weight during this time, digging dens on land in August or September and going into something akin to hibernation.
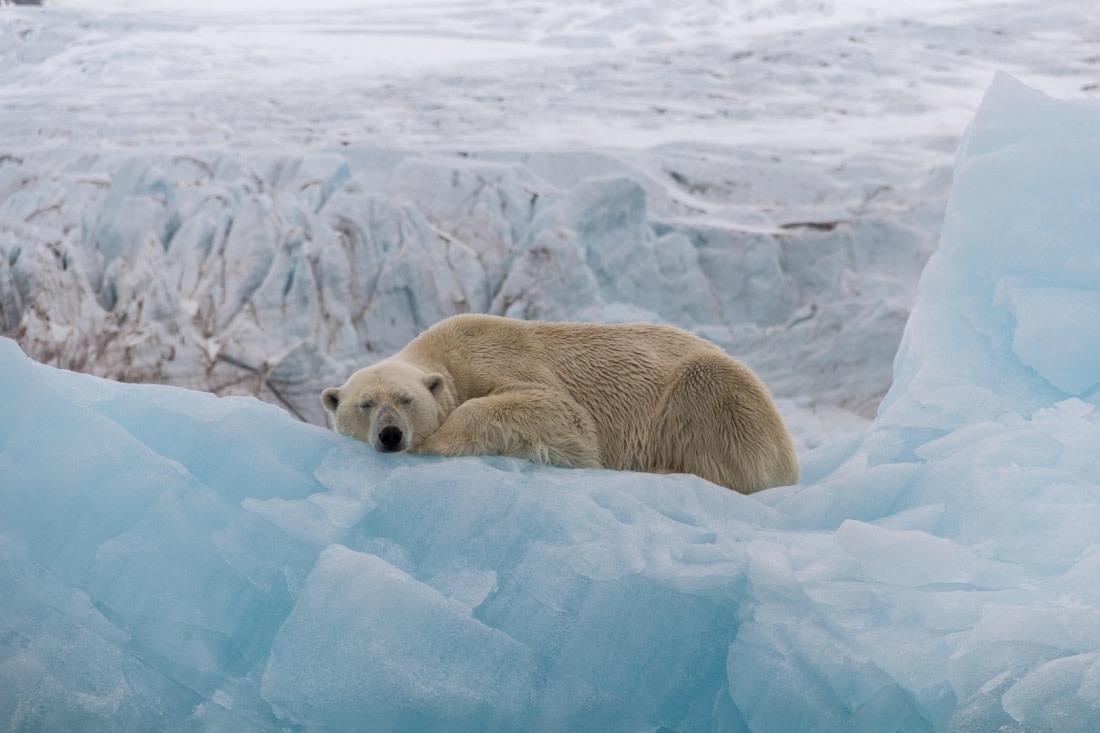

Though polar bear females regularly wake during this time and their temperatures don't drop to the degree other bear species do during hibernation, their heart rate does slow from an average of 45 beats per minute to about 25 beats.
Female polar bears give birth to two cubs at most between November and February. Polar bear cubs are born blind and usually weigh around 1 kg (2.2. pounds). Mothers stay holed up in their dens and nurse the cubs until mid-February or mid-April, then spend another 10 to 15 days close to the den until the bear cubs are used to the outside world.
After this, the polar bear family typically travels back to their seal hunting grounds.

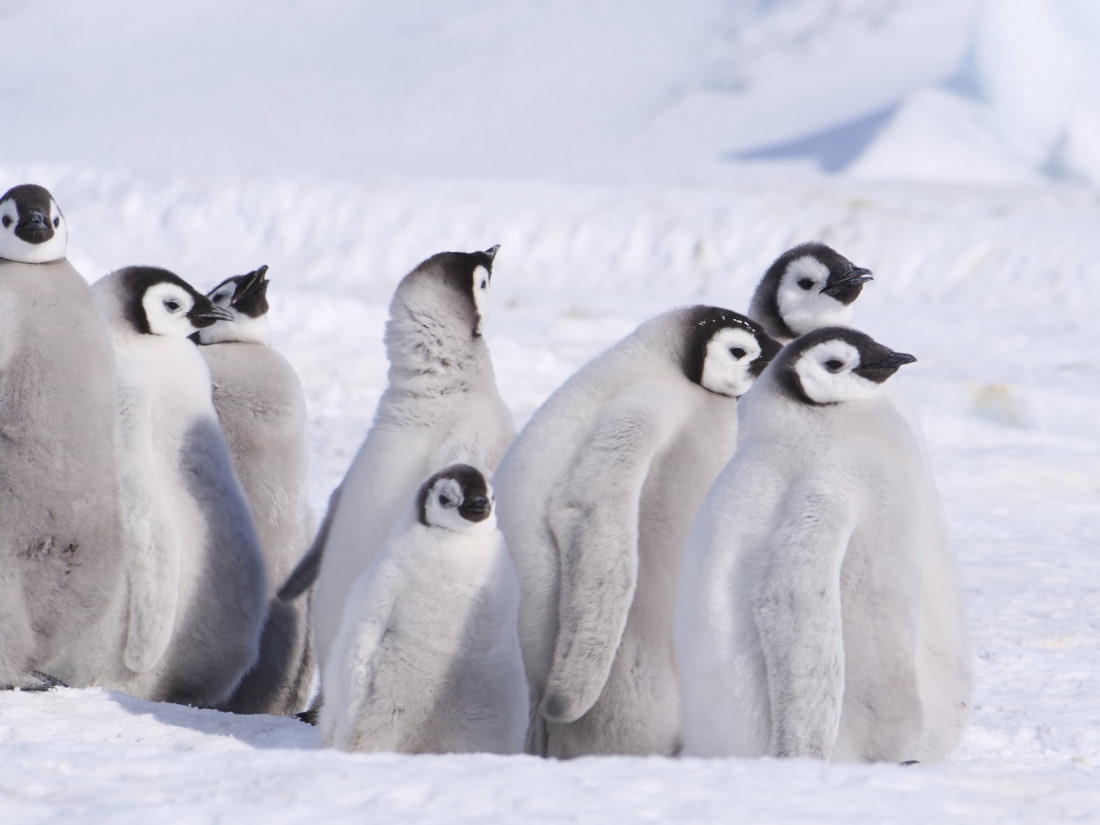
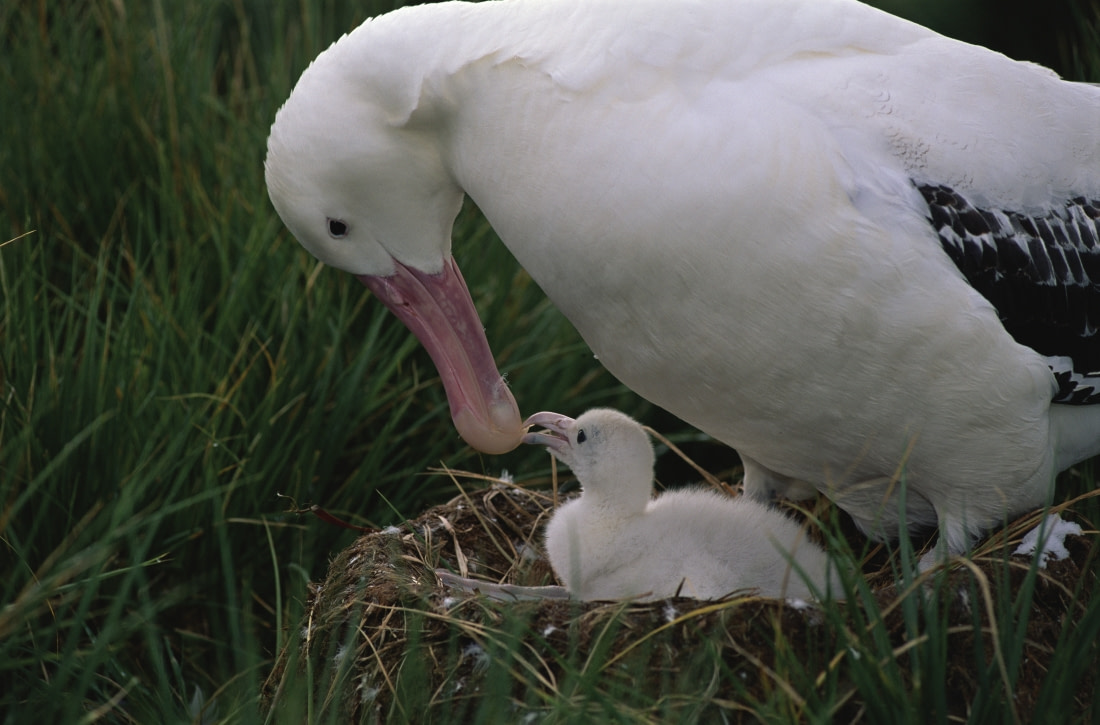
2. How emperor penguins play nug-a-nug
Emperor penguins have the distinction of being the only penguin species to breed during Antarctica's winter season. They hit the ground running even earlier than polar bears, becoming sexually mature at age three.
Beginning in April, emperor penguins start the long march to their breeding grounds. This often means traveling anywhere from 50 km (30 miles) to more than 150 km (over 90 miles) across the harsh Antarctic terrain.
All of this hard travel pays off in May: Male emperor penguins arrive ahead of the females, wooing their future mates by pushing their bills to their chests and sounding off a mating call that lasts for about two seconds. Once couples have paired up, they stand still and extend their necks upward, staring at each other for several minutes.
This solemn spectacle marks the official start of their relationship, after which they begin the breeding process by bowing deeply to each other.
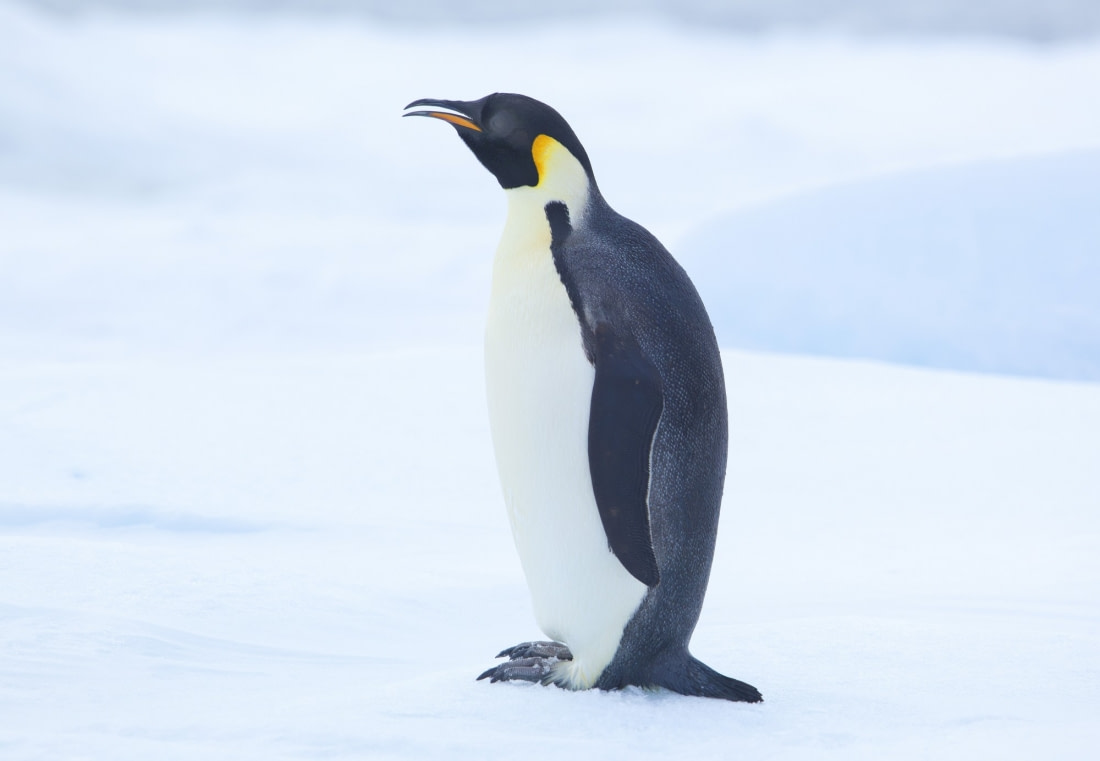

Emperor penguins are serially monogamous, staying with one mate for the entire season but usually choosing a different one the next season. Females produce a single egg, then males incubate it by placing the egg on their feet (and keeping it warm with a skin flap) while females leave to replenish the weight they lost during pregnancy.
Male emperors do not eat during incubation, losing a lot of weight themselves. To conserve heat, they often huddle together with their backs to the wind.
Females return around the beginning of August, locating their mates by their particular calls. They then take over feeding the chick, and a month and a half later emperor penguin chicks are ready to leave their mothers and form small chick groups called crèches.

3. The walrus way of shooting twixt wind and water
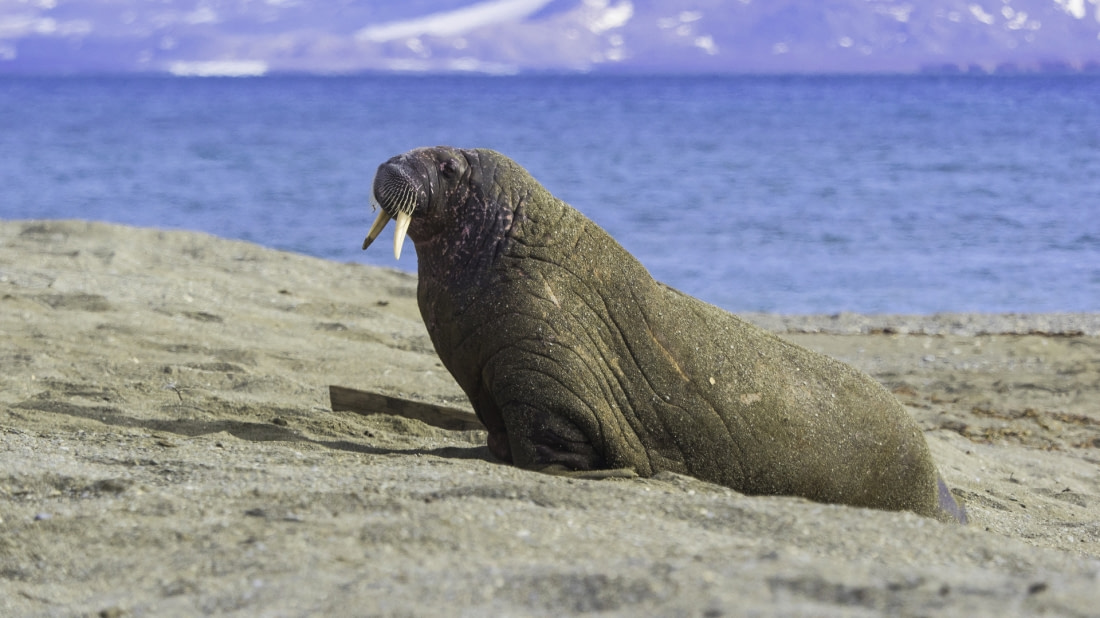
You might see walruses, like polar bears, on some of our select Arctic cruises. But walruses may have it even tougher than their polar bear neighbors when it comes to breeding competion: Although males are sexually mature around age seven, they're usually not strong enough to best other male walruses for mating privileges until they're about 15 years old.
Is anyone else reminded of high school?
Females, however, are good to go by age four. From January through March, walrus males fight each other for access to these females. Lads that come out on top swim around the females, projecting vocal calls from large air sacks under their throats.
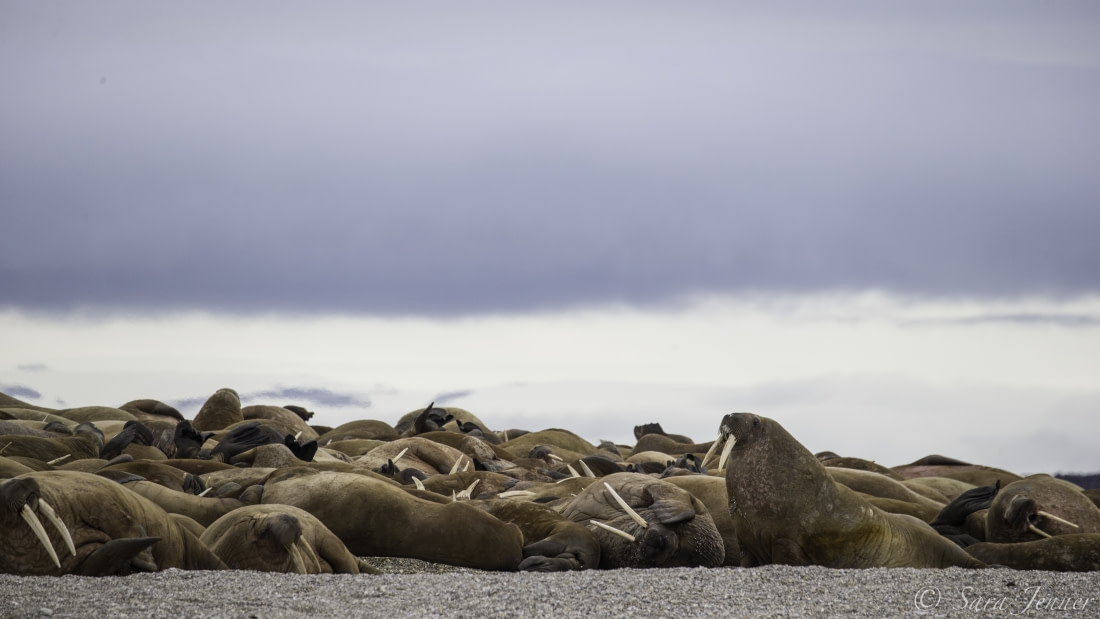

Once the breeding deed is done, pregnancy lasts about 15 months.
Calving occurs during the spring migration (April through June) of the following year, and newborn walrus pups are born immediately able to swim. Mothers still nurse them for over a year, however, and the young walruses stay with their mothers for up to five years.
Given the walrus lifespan, that's the human equivalent of being independent at about 16 - 20 years old. Millenials, take a lesson from this.

4. Wandering albatrosses blowing off the groundsills
Wandering albatrosses live to be about 50 years old in the wild and reach sexual maturity around 11, meaning that if they were human they'd be hitting the nightclubs by their 22nd birthday - a conservative number by most estimates.
Less conservative are their breeding practices: Courting male albatrosses show interest by spreading their wings, waving their heads, and rapping their bills against those of the females while making loud braying noises.
Try that in the club and see how fast security responds.
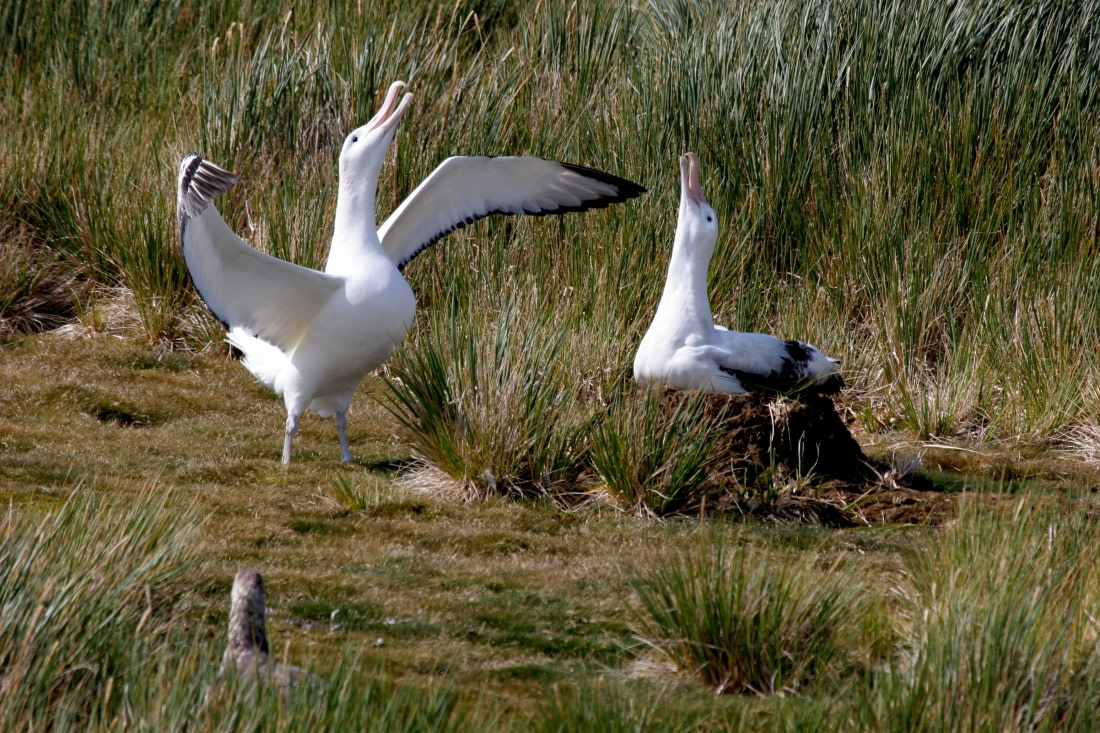

Naturally, breeding rituals of such rare sentimentality lead to lifelong bonding. Wandering albatrosses mate for life, doing the dirty every two years. Their mating season starts in early November, when albatrosses create nests of mud and grass on the sub-Antarctic islands.
Females lay one egg between the middle of December and early January, after which incubation takes around 11 weeks. Once the wandering albatross chick is born, adults switch off between hunting and staying at the nest to care for the chick.
The hunting parent regurgitates stomach oil for the chick to feed on, but eventually both parents will hunt at the same time and visit the chick less and less.
You may see these seabirds (and emperor penguins) on one of our Antarctica trips.

5. How humpback whales make the beast with two backs
Humpback whales can be spotted in both the Arctic and Antarctica, making them a fitting climax to this list. So to speak.
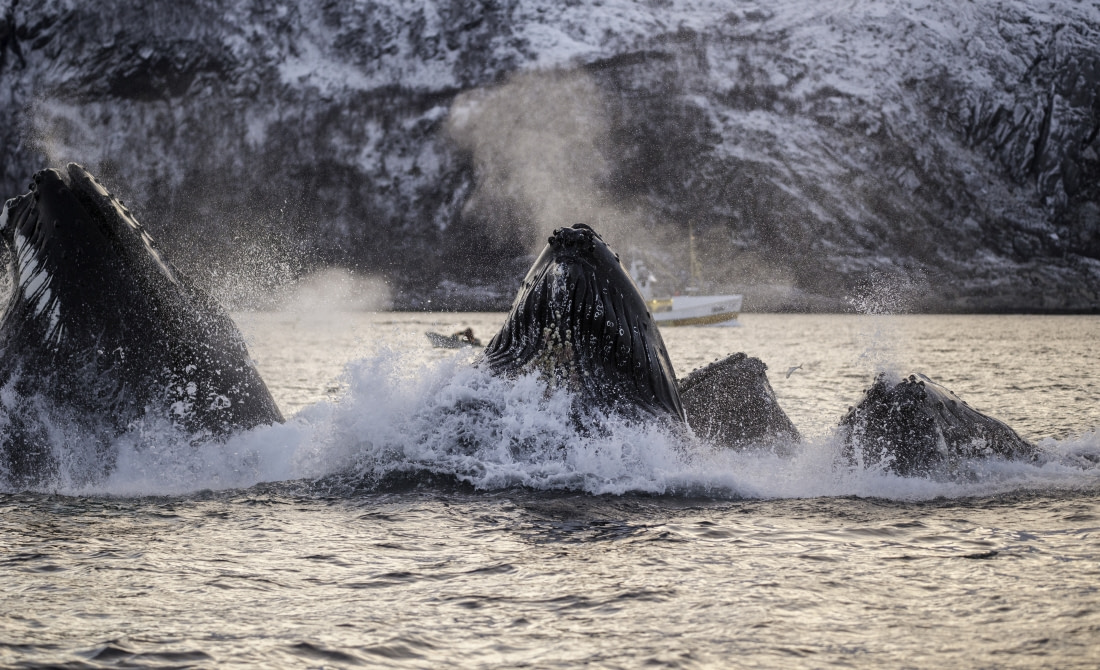
Females flash the green light by age five, but male humpbacks don't notice it until seven. And like most other animals on this list, males gather into groups to battle for dominance. These frothy fights may include breaching, charging, and "spy-hopping," which is when whales float with their heads above water. Humpbacks with mating on the mind might also engage in lob-tailing, slapping the water with their flukes to create a loud and intimidating sound.
Mating occurs in the tropics during the winter months, after humpback whales have migrated away from their summer feeding areas.
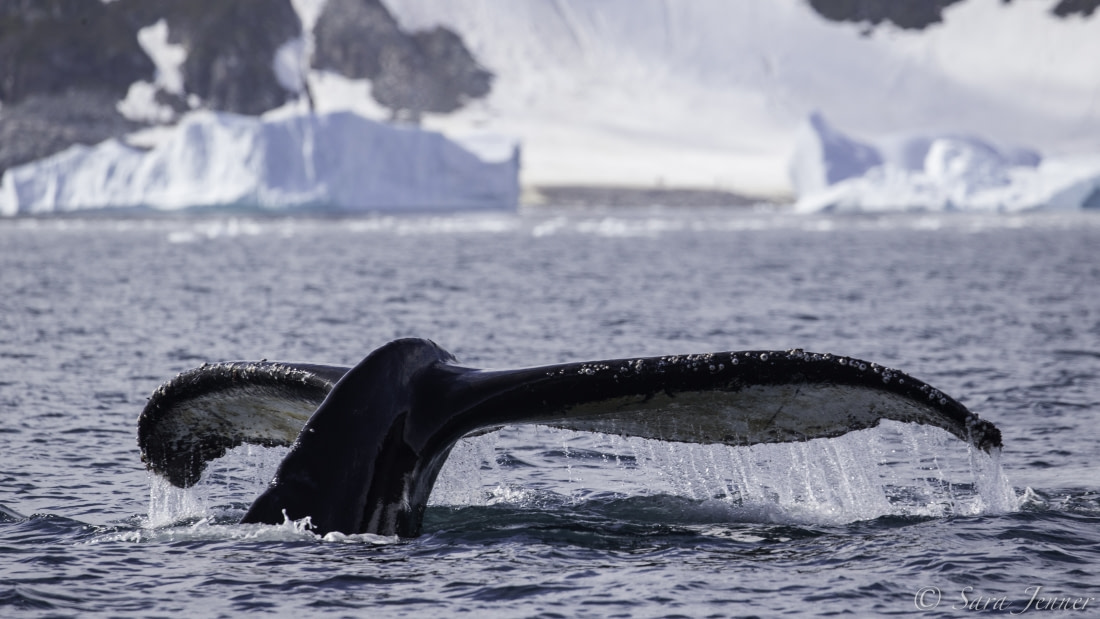

Pregnancy lasts about 11 months, after which humpback calves come out weighing about 900 kg (almost 2,000 pounds) and are roughly 3 to 4.5 meters (10 to 14.7 feet) long.
And not surprisingly, something that big arrives with a hunger hardly to be believed. Humpback whale calves drink 45 kg (100 pounds) of milk each day until they're weaned about six months later, which puts them just behind the volume of food consumed by the average college student raiding their parents' fridge at 2am.
But like these polar animals will tell you, that's all part of the joy of procreation.

Blog



5 Life Lessons You'll Learn in Antarctica

Six Seal Species You Might See On Your Greenland Cruise

Arctic and Antarctic Basecamp Cruises – Choose Your Own Adventure

Flowers in Antarctica

Five Reasons You Should Cruise the Ross Sea Immediately

Under the Greenland Ice Sheet

Graham Land: A landscape dominated by volcanoes

Life migrating through the Polar Front

Where the Polar Bears Roam

The Ins, Outs, and Ups of Polar Mountaineering & Ski Mountaineering

Inside the Svalbard Global Seed Vault

Polar bear feast

North Norway, Northern Lights, and All the Pretty Whales

Svalbard’s Texas Bar

Harp seals harping on in Greenland

Arctic Mythology: Inuit, Saami, and the Ancient Greeks

The secrets of Antarctic seals revealed

The Secret Life of Glaciers: How They Form, Move, and Melt

Earth vs. Mars: Polar Regions Compared